Sodium borate, commonly known as sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate, is an important boron chemical. Borax is another common name for sodium borate. It has a white tint in powdered form, with a composition of brittle colorless crystals. These crystals are water soluble, and sodium borate, in addition to being a boron compound, is also a mineral that acts as a salt of boric acid.The term “borax” means “octahydrate.” According to the article, borax is a group of chemical compounds that are identical in composition but varies in the amount of crystal water they contain. The borax we buy in supermarkets and local stores is partially dehydrated.
Borax Chemical Formula and Structure :
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate is the IUPAC designation for sodium borate. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is an organisation that promotes the study of pure and applied chemistry.
The fact that sodium borate comes in two distinct forms is undeniable. Each one is distinct and plays a vital function in chemistry.
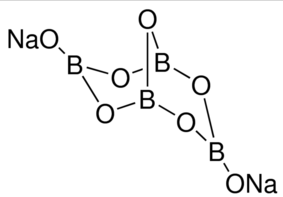
One state is the hydrated state, in which the hydration water appears to be active. There is no water of hydration in the dehydrated form of sodium borate. Na2B4O7 is its chemical formula.
The molecular weight of this molecule is 381.4 g/mol, and it has a trigonal structure (hydrated state).Three positively charged ions can be seen in the structure, which are attracted to the borate ion. They create ionic bonds as a result of this force.Borate is a covalent combination of boron and oxygen that fuses to generate boron oxyanion, as we already know. It’s also possible to deduce that the structure is tetrahedral.
Chemical properties:
- The nature of sodium borate is stable. When borax is present near glass, it does not promote corrosion.
- Borax is incompatible with alkaloidal salts, mercuric chloride, zinc sulphate, and other metallic salts, as well as moisture.
- Borax reacts strongly with acids when it is present in its hydrated state. When the chemical combines with acids, it produces boric acid.
- Borax has a great solubility when it comes to ethylene glycol.
- In nature, sodium borate is combustible. When sodium borate is burned, it produces a greenish flame with a yellow hue.
- It interacts with bases and is only slightly soluble in acetone.
Boric acid:
Boric acid, also known as hydrogen borate, boracic acid, and orthoboric acid, is a boron Lewis acid that is weak and monobasic. However, its behavior in certain chemical reactions suggests that it is also tribasic acid in the Bronsted sense. Boric acid is frequently employed as an antiseptic, pesticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, or chemical precursor. It is a colorless crystal or a white powder that dissolves in water with the chemical formula H3BO3 (occasionally spelled B(OH)3). It’s known as sassolite when it’s found as a mineral.
Uses:
- When it comes to cleaning and laundry, borax is a common household staple. It’s also found in certain soaps as a general ingredient. Borax is frequently used by dentists to carry out teeth whitening treatments.
- Borax is frequently used in chemical laboratories to generate buffers in the form of boric acid. It’s also utilised as a solution in dimethyl pimelimidate.
- Borax is also used as a food preservative to improve the flavour and look of food. It also helps to preserve food in a stable state.
- Borax is being used to extract gold in small-scale mining facilities in several nations, such as the Philippines. This procedure is also known as the borax method.
- Borax is also employed in several treatment plants as a water softening agent.
Overexposure to borax:
- A high dose of sodium borate can have serious side effects, including severe symptoms and even death.
- When exposed to borax for an extended period of time, the respiratory tracts can get irritated.
- This chemical can produce nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and stomach pain if consumed.
- Headaches and weariness are caused by this condition, which affects the nerve system.
- Rashes on the palms, soles, and private regions of the body are possible side effects.
- Over time, excessive ingestion of borax might lead to liver cancer.
Conclusion:
The chemical compound sodium borate is colourless. It’s also known as sodium tetrahydrate or borax. Borax reacts strongly with acids and has a wide range of applications.Sodium borate is found in nature in the form of deposits in seasonal lakes. Because the lakes are exposed to lengthier periods of evaporation, this occurs.Sodium borate has a white colour and is easily dissolved in water. It has a high solubility in ethylene glycol and is stable.Sodium borate is a common ingredient in cosmetics, as well as a cleaning agent, a water pH controller in swimming pools, a food preservative, a teeth whitening agent, and a woodwork treatment. It also serves as a cure for snake skins and, in some cases, aids in the extraction of gold.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out