It is based on the octet rule, according to which atoms share electrons in order for each atom to have eight electrons in its outer shell, that a Lewis structure is formed. In the outer shell of an oxygen atom, for example, there are six electrons total. Using a Lewis structure, the arrangement of these six dots results in an atom possessing two lone pairs and two single electrons. When viewed around the O symbol, the two electron pairs would be in opposition to each other, and when viewed from either side of the atom, they would be in opposition to each other.
In most cases, single electrons are represented by a symbol on the side of an element symbol. An example of incorrect placement would be (for example) four electrons on one side of the atom and two on the other side of the atom.The simplest example is hydrogen (H), which has one proton and one electron and is the smallest element in the periodic table. If it achieves a complete valence level, like the noble gas closest to it in the periodic table, helium, it can become stable (He). Because they only require two electrons to have a complete valence level, these are exceptions to the octet rule.
To form a ‘covalent bond,’ two H atoms can come together and share each of their electrons. Each atom now has two electrons in its valence level, similar to He, because the shared pair of electrons can be regarded as belonging to either atom. H2 is the most abundant molecule in the universe as a result of this process.
Lewis structure of CO2
When carbon is burned, it produces carbon dioxide, which is a colourless, odourless, and incombustible gas. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO2 molecule is 1:2. The carbon and oxygen atoms are connected by two double bonds in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms at the terminals can share electrons with the central carbon atom and form bonds with it.
Lewis structure diagrams depict the number of valence electrons that are available for bond formation within an atom in a given state. It also allows for the visualisation of the behaviour of the valence electrons within the molecule, as well as the determination of whether or not a lone pair of electrons exists within the molecule itself.
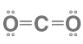
Lewis Structure of O2
Bonds between O atoms will appear as two lines appear between them. We’re dealing with a double bond here. Each O atom needs two electrons to make a link. The two parallel lines symbolise the four electrons that make up the double bond.
In the O2 double bond, each O is encircled by four dots and two lines, which indicate another four electrons. The upshot is that the octet of valence electrons around each O is stable since it has 8 total valence electrons.
The oxygen atoms’ nuclei are represented by the O2 Lewis structure’s two letter Os. Protons and neutrons, the molecule’s solid constituents, are housed in the nucleus. Even though electrons are a non-solid particle, the dots and lines in this image represent them. A pea in a stadium compared to the electrons around it is the usual size of the nucleus in this picture.
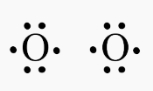
Lewis structure of CO
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic gas that has no odour or colour and can be detected with the naked eye. Because of the way it is constructed, it has two unique atoms: carbon and hydrogen. It’s a polar molecule with bond angles that are 180 degrees. There is a triple bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms in this compound. The carbon monoxide molecule has a total of ten valence electrons in its structure.

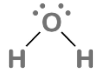
Lewis structure of H2O
The molecular formula for water, one of the most important substances of the Earth, is H2O. In order for water to exist, it must include two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, all of which are linked together by a covalent connection. A compound is formed when two or more H2O molecules link together through the formation of hydrogen bonds.
The term “electron dot structure” refers to a similar structure. An atom’s valence electrons can be counted in order to determine the total amount of valence electrons that are available for bonding in order to create molecules and compounds. Either the electron dot structure or the Lewis structure are other names for the same structure.
Conclusion
It is based on the octet rule, according to which atoms share electrons in order for each atom to have eight electrons in its outer shell, that a Lewis structure is formed. In most cases, single electrons are represented by a symbol on the side of an element symbol. An example of incorrect placement would be (for example) four electrons on one side of the atom and two on the other side of the atom.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




