The process by which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment is known as respiration. All living organisms, from prokaryotic bacteria and archaeans to eukaryotic protists, fungi, plants, and animals, respire.
To begin, respiration can refer to either external respiration or the process of breathing (inhalation and exhalation), which is also known as ventilation. Second, respiration can refer to internal respiration, which is the movement of gases through body fluids (blood and interstitial fluid) and tissues. Finally, respiration may refer to the metabolic processes that convert the stored energy in biological molecules to usable energy in the form of ATP. This process may involve the consumption of oxygen and the production of carbon dioxide, as seen in aerobic cellular respiration, or it may not, as in anaerobic respirations.
Respiration
All living organisms require energy to perform various tasks and to sustain life. This energy is obtained from food through a process known as respiration. Cells in animals produce chemical energy from the degradation of organic compounds, whereas plants produce decomposed food from the photosynthesis process.
Thus, respiration is a critical biochemical oxidation reaction process in which food materials are oxidised to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
Types of Respiration
We distinguish two types of respiration based on the presence or absence of oxygen:
Aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen because it uses ‘air,’ which contains oxygen. Aerobic respiration involves the use of oxygen to break down chemical bonds in glucose, releasing a large amount of energy. It is the most important source of energy for both plants and animals. Aerobes are animals and plants that use oxygen to breathe. Aerobic respiration is used by the vast majority of animals.
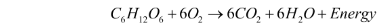
All organisms that obtain energy through aerobic respiration cannot survive in the absence of oxygen. This is due to the fact that if there is no oxygen, they will not be able to obtain energy from the food they consume. Aerobic respiration generates more energy because it involves the complete breakdown of glucose through the use of oxygen.
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. In this process, food material undergoes incomplete oxidation, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide and alcohol. Aside from this, organic matter such as citric acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid, and others are produced.
This is also referred to as intramolecular respiration. Anaerobic respiration occurs in organisms such as yeast, some bacteria, and parasitic worms. Anaerobic animals and plants can survive and produce energy even in the absence of oxygen.
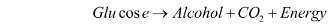
Yeast is a fungus with a single cell. A single cell in yeast represents the entire organism. This process uses a very small amount of energy. Yeast respires anaerobically, and during this process, glucose is converted into alcohol. As a result, it is used to make alcohol bread, among other things.
Anaerobic respiration produces significantly less energy because the only partial breakdown of glucose occurs in the absence of oxygen. All organisms that obtain energy through anaerobic respiration can survive in the absence of oxygen.
For example, yeast is an organism that can survive in the absence of oxygen because it obtains energy through the process of anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, yeast can survive.
Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles
Humans normally obtain energy through aerobic respiration. However, anaerobic respiration can occur in our muscles for a short period of time when we require extra energy. When we engage in strenuous physical activity, our muscles require more oxygen. However, the supply of oxygen via blood is limited and thus insufficient.
Some of our muscles breathe anaerobically during strenuous exercise. Muscle anaerobic respiration results in the partial breakdown of glucose to form lactic acid. Lactic acid build up in the muscle. Muscle cramps are caused by an accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles.
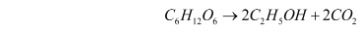
Yeast are organisms with one cell. They respire anaerobically, producing ethyl alcohol, which is used to make wine and beer. They are also employed in the baking industry.
In animals
Our muscles require oxygen and glucose in order to respire aerobically and produce the energy they require; these are delivered to the muscle via the blood. However, if we performed vigorous exercise, our heart and lungs would not be able to deliver enough oxygen to our muscles to allow them to breathe. Muscles perform anaerobic respiration in this case. The term and chemical equation for anaerobic respiration in are as follows:
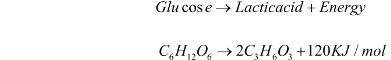
As can be seen, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic respiration, and only a small amount of energy is released. This is due to the fact that glucose can only be partially broken down. In addition to this inefficiency, lactic acid, a poisonous chemical, is produced; if this accumulates in the body, it prevents the muscles from working and causes the cramp. The amount of oxygen required to break down the lactic acid is referred to as the oxygen debt, and it is required to rid the body of lactic acid.
In Plants
Plants’ oxygen supply can also be depleted, for example, if the soil becomes waterlogged. In this case, they must obtain energy through anaerobic respiration. The word and chemical equation for anaerobic respiration in plants are as follows:
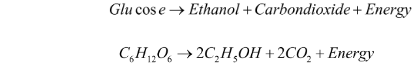
Fermentation occurs when the above reaction occurs in yeast cells. Fermentation is the process by which bread is baked and alcohol is brewed.
Conclusion
The process by which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment is known as respiration. All living organisms, from prokaryotic bacteria and archaeans to eukaryotic protists, fungi, plants, and animals, respire. . Cells in animals produce chemical energy from the degradation of organic compounds, whereas plants produce decomposed food from the photosynthesis process. Respiration is a critical biochemical oxidation reaction process in which food materials are oxidised to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. . Aerobic respiration involves the use of oxygen to break down chemical bonds in glucose, releasing a large amount of energy. Anaerobic respiration is respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. In this process, food material undergoes incomplete oxidation, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide and alcohol. When we engage in strenuous physical activity, our muscles require more oxygen. . The amount of oxygen required to break down the lactic acid is referred to as the oxygen debt, and it is required to rid the body of lactic acid. Plants’ oxygen supply can also be depleted, for example, if the soil becomes waterlogged. In this case, they must obtain energy through anaerobic respiration.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




