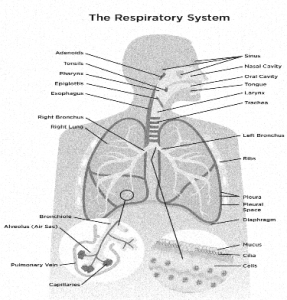
The respiratory system begins with the nose and mouth and progresses to the airways and lungs. Air enters the respiratory system via the nose and mouth, then travels down the throat (pharynx) and into the voice box, or larynx. A small flap of tissue (epiglottis) covers the entrance to the larynx and closes automatically during swallowing, preventing food or drink from entering the airways.
Respiratory system-
- Ventilation, external respiration, gas transport, internal respiration, and cellular respiration are all part of the respiration process.
- Atmospheric pressure, intra alveolar pressure, and intrapleural pressure are the three pressures responsible for pulmonary ventilation.
- A spirometer is used to measure the volume and capacity of the lungs. These measurements provide important information about the health of the lungs.
- The air-filled cavities that open into the nasal cavity are known as the frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal sinuses.
- The pharynx, also known as the throat, is a passageway that runs from the base of the skull to the sixth cervical vertebra.
- The larynx, also known as the voice box, is the airway that connects the pharynx above and the trachea below.
- The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is the primary airway to the lungs.
- The trachea is divided into the right and left primary bronchi, which branch into smaller and smaller passageways until they reach tiny air sacs known as alveoli.
- Beyond the primary bronchi, the two lungs contain all of the bronchial tree’s components.
- The right lung is narrower and broader, with three lobes.
- The left lung is longer and narrower, with two lobes.
Lungs-
The lungs absorb oxygen. The cells in your body require oxygen to live and function normally. Carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells, is also expelled by the lungs.
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made of pinkish-gray spongy tissue. They occupy the majority of the chest space (thorax).
A membrane surrounds the lungs (pleura).
Respiration is the act of breathing
Inhalation and exhalation are the processes by which your body takes in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. The diaphragm, a large dome-shaped muscle beneath your lungs, aids in the process.When you breathe in, your diaphragm pulls downward, creating a vacuum and allowing air to rush into your lungs.When you exhale, your diaphragm relaxes upward, pushing on your lungs and allowing them to deflate.
What is the process by which the respiratory system cleans the air?
Your respiratory system has mechanisms in place to prevent harmful substances in the air from entering your lungs.
Large particles are filtered out by the hairs in your nose. Tiny hairs called cilia move in a sweeping motion along your air passages to keep them clean. However, if you breathe in harmful substances, such as cigarette smoke, the cilia may stop working. This can result in health issues such as bronchitis.
Cells in your trachea and bronchial tubes produce mucus, which keeps air passages moist and keeps dust, bacteria, viruses, and allergy-causing substances out of your lungs.
Mucus can bring things up from deeper within your lungs.
Respiratory system diseases-
The following are examples of common respiratory diseases:
- Asthma. Your airways are congested and produce an excessive amount of mucus.
- Bronchiectasis. Inflammation and infection thicken the bronchial walls.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (COPD). This long-term condition worsens with time. Bronchitis and emphysema are examples.
- Pneumonia. Your alveoli become inflamed as a result of an infection. They could become clogged with fluid or pus.
- Tuberculosis. This dangerous infection is caused by a bacterium. It usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect the kidney, spine, or brain.
- Cancer of the lungs. Lung cells change and grow into a tumour. This is frequently caused by smoking or other chemicals inhaled.
- Cystic fibrosis. This disease is caused by a genetic problem and worsens over time. It causes persistent lung infections.
- Pleural effusion. A lot of fluid accumulates between the tissues that line your lungs and chest.
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Your lung tissue becomes scarred and unable to function normally.
- Sarcoidosis. Granulomas are tiny clumps of inflammatory cells that form in your lungs and lymph nodes.
Conclusion
The respiratory system begins with the nose and mouth and progresses to the airways and lungs. Air enters the respiratory system via the nose and mouth, then travels down the throat and into the voice box, or larynx. A spirometer is used to measure the volume and capacity of the lungs. The pharynx, also known as the throat, is a passageway that runs from the base of the skull to the sixth cervical vertebra. The larynx, also known as the voice box, is the airway that connects the pharynx above and the trachea below. The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is the primary airway to the lungs. Beyond the primary bronchi, the two lungs contain all of the bronchial tree’s components.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






