The sequence of exchanges of materials and energy in the form of food from one organism to another is referred to as the food chain in ecology. Because most species ingest more than one type of animal or plant, food chains and food webs interact locally to form a food web. The primary food source is plants, which turn sun energy into food through photosynthesis. A plant-eating animal is eaten by a flesh-eating species in a predatory chain. A tiny creature consumes a portion of a larger host and may be parasitized by even smaller species in a parasite chain. Microorganisms in a saprophytic chain feed on dead organic substances.
Types of Food Chain
- Grazing Food Chain : This food chain begins with living green plants, then moves on to grazing herbivores, and finally to carnivores. Ecosystems with this type of food chain are completely reliant on sun radiation.
As a result, this type of cycle is reliant on autotrophic energy capture and the transfer of that energy to herbivores. This form of food chain is seen in the majority of natural ecosystems. Grazing food chains include phytoplanktons→ zooplanktons → fish sequences and grass → rabbit → fox sequences, for example.
- Detritus Food Chain : This sort of food chain starts with dead organic matter, then moves on to microorganisms, detritus-feeding creatures (detritivores), and predators. As a result, such ecosystems are less reliant on direct solar energy. These are mostly reliant on the inflow of organic materials generated in another system. In a temperate woodland, for example, such a food chain can be found digesting accumulated litter.
Significance
- Food chain research aids in understanding the feeding relationship and interactions among organisms in any ecosystem.
- They also assist us in appreciating the energy flow mechanism and matter circulation in ecosystems, as well as understanding harmful material migration.
- The study of the food chain aids in the comprehension of bio-magnification issues.
Classification of Grazing Food Chain :
Predator Chain : In this case, one animal eats another. The prey is the animal that is being eaten, and the predator is the animal that is eating the prey.Plants start the energy cycle because they use sunshine and soil to make food. Animals, on the other hand, are energy consumers because they eat other plants and animals.
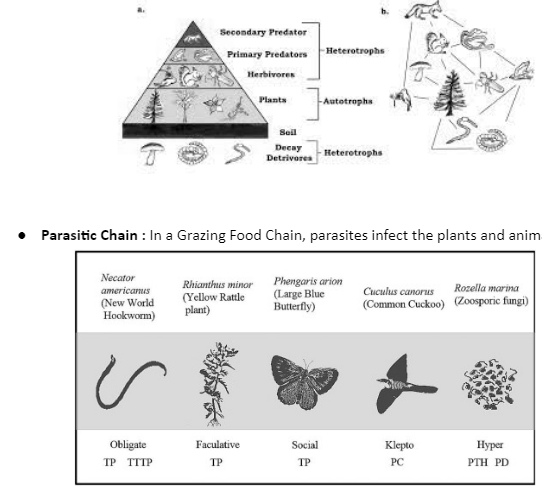
Features of the Grazing Food Chain
- The sun, which is a key source of energy in this food chain, is extremely important to the grazing food chain.
- Plant oxidation, virus assault, and plant decay owing to increased water flow are some of the elements that affect this food chain.
- This food chain contributes energy to the environment and aids in the fixation of inorganic nitrogen in the soil.
- Every macroscopic organism is participating in this food chain, which is all species that can be seen with the naked eye.
Difference between the two types of food chains
Parameter | Detritus Food Chain | Grazing Food Chain |
Based on | Decomposers or detritivores | Photosynthetic plants |
Basis | Decomposers | Plants |
Primary Energy | Remains of plants and animals | Green plants or producers |
Scope | Small | Large |
Energy | Emits energy to the environment | Utilises energy from the environment |
Organisms | Microorganisms | Plants and animals |
Energy Flow
In the grazing food chain, energy flows in the following manner:
- Trophic levels, which signify an organism’s place in the food chain, are a representation of energy flow in an ecosystem.
- The food chain’s energy flow is unidirectional.
- Because of the creation of heat at each trophic level, energy will decrease.
- As a result, energy loss is widespread in the food chain, resulting in a food chain with only a few trophic levels (beyond that level no organism will get an adequate amount of energy to survive).
Example
Phytoplanktons are eaten by zooplanktons, which are eaten by fish, and tiny fishes are devoured by huge fishes. Rabbits consume the grasses, and the rabbit is eaten by a fox. A deer eats the little plants or grass, and the deer is afterwards eaten by a lion.
Conclusion
The food chain is a diagram that depicts the transmission of energy in the form of food from one organism to another. Grazing food chains and Detritus Food Chains are the two types of food chains. Autotrophs are the principal producers of food in the grazing food chain, whereas subsurface organisms devour dead animals in the detritus food chain. The interconnectedness of numerous food chains in an environment with variable energy flow levels is known as the food web.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




