The two types of white blood cells found in blood are granulocytes and agranulocytes. Leukocytes are another name for white blood cells. They are the first line of defence in the battle against disease. Granulocytes include eosinophils, neutrophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes are monocytes and lymphocytes. The most active phagocytes are neutrophils and monocytes, which engulf and eliminate invading infections. T and B lymphocytes are important in identifying antigens present in antigen-presenting cells in order to develop specific antibodies against a specific infection. Granulocytes and agranulocytes are distinguished by the presence of granular cytoplasm in granulocytes and the absence of granular cytoplasm in agranulocytes.
Granulocytes
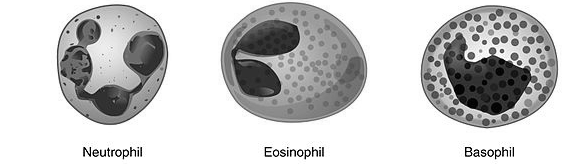
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are the three types of granulocytes. When dyed, the granules of these white blood cells can be observed under a microscope.
- Neutrophils : The nucleus of these cells is a multiple lobed nucleus. Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell in the body. They are attracted to bacteria chemically and move through tissue to infection locations. Neutrophils are phagocytic, which means they eat and kill target cells. Their granules act as lysosomes when released, digesting cellular macromolecules and killing the neutrophil in the process.
- Eosinophils : In blood smears, the nucleus of these cells is double-lobed and appears U-shaped. Eosinophils are commonly located in the stomach and intestines’ connective tissues. Antigen-antibody complexes generated when antibodies bind to antigens to signal that they should be eliminated are the primary focus of these phagocytic cells. During parasite infections and allergic reactions, eosinophils are at their most active.
Basophils : Heparin, an anticoagulant found in basophils, stops blood from clotting too quickly inside blood arteries. During asthma, the enzymes in their granules are also released. In comparison to other granulocytes, basophils are the least abundant in the blood. Basophils, on the other hand, are the largest granulocytes.
Agranulocytes
Agranulocytes, or nongranular leukocytes, are divided into two types: lymphocytes and monocytes. There are no granules seen on these white blood cells. Agranulocytes have a bigger nucleus than granulocytes because they lack cytoplasmic granules.
- Monocytes : By developing into macrophages, monocytes can migrate into contaminated organs. They have the ability to develop into dendritic cells. Monocytes play a role in an organism’s innate immunity, acting as the host’s first line of defense. They also produce an inflammatory reaction, which activates the adaptive immune system. Cytokines and chemokines are released by monocytes. Monocytes respond to inflammation by migrating into tissue within 8-12 hours.
Lymphocytes : Lymphocytes are the most prevalent form of white blood cell after neutrophils. These cells have a spherical shape, big nuclei, and a small amount of cytoplasm. T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells are the three main types of lymphocytes. T cells and B cells are required for specialised immune responses, while natural killer cells provide general immunity.

Comparison
Parameter | Granulocytes | Agranulocytes |
Granules | Has granules | No granules present |
Leukocytes % | 65% | 35% |
Immunity | Has Innate Immunity | Has Adaptive Immunity |
Origin | Bone marrow | Lymphoid |
Other name | Polymorphonuclear leukocytes | Mononuclear leukocytes |
No. of Lobes | 2-6 | 1 |
Conclusion
The two forms of leukocytes found in blood are granulocytes and agranulocytes. The presence of granular cytoplasm, which is coloured differently under a light microscope, distinguishes them. Membrane-bound enzymes in these granules predominantly degrade phagocytized particles. The three types of granulocytes are eosinophils, neutrophils, and basophils, which may be distinguished by the staining qualities of the granules in the cells. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes are another name for granulocytes. Despite the absence of cytoplasmic granules, agranulocytes contain non-specific azurophilic granules such as lysosomes. Agranulocytes are divided into three types: monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes. Mononuclear leukocytes are another name for agranulocytes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




