Mitochondria serve as energy-producing powerhouses, they are abundant in places where energy is required in large quantities, such as the sperm tail, muscle cell, liver cell (which can contain up to 1600 mitochondria), microvilli, and the oocyte (which can contain more than 300,000 mitochondria).
In most cells, there are approximately 2000 mitochondria per cell, which accounts for approximately 25% of the total cell volume.
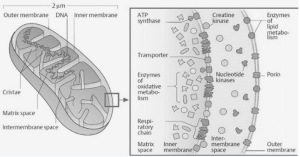
Richard Altmann published the first description of mitochondria in 1890, referring to them as “bioblasts.” Benda first used the term “mitochondria” in 1897, when he published a paper on the subject. Mitochondria are organelles that are mobile and plastic, and they have a double-membrane structure. It has a diameter that ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometer. It is divided into four different contexts: the outer membrane, the inner membrane, the intermembrane space, and the matrix.
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are oxygen-consuming, ribbon-shaped cellular organelles that float freely throughout the cell and play a critical role in energy production.
- They are referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell” because they are responsible for supplying the cell with all of the necessary biological energy by oxidising the substrates that are available.
- The enzymatic oxidation of chemical compounds occurs in the mitochondria, resulting in the production of energy.
Structure of mitochondria
- In addition to the smooth outer membrane, the organelle is surrounded by a markedly folded or tubular inner mitochondrial membrane, which has a large surface area and encloses the matrix space.
- The intermembrane space is the space that exists between the inner and outer membranes of a membrane cell.
- The number and shape of mitochondria, as well as the number of cristae present in them, can vary significantly from one cell type to another.
- Muscle tissue and other tissues that have a high rate of oxidative metabolism, such as heart muscle, have mitochondria with a particularly high number of cristae.
- When the mitochondria are in different states of function, even within one type of tissue, the shape of the mitochondria can change.
- Both mitochondrial membranes contain a high concentration of proteins
Functions of mitochondria
- The production of energy is the most essential function of the mitochondria. Mitochondria are responsible for the production of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which serves as one of the cell’s energy currencies, providing the energy necessary to drive a variety of cellular reactions and mechanisms.
- The mitochondria are responsible for processing and producing charged molecules from the simple substances of nutrition that are consumed. When these charged molecules combine with oxygen, they form ATP molecules, which are used for energy production. Oxidative phosphorylation is the term used to describe this process.
- Besides producing heat (brown fat), mitochondria can also accumulate iron-containing pigments (heme ferritin), calcium ions (Ca2+), and phosphate ions (HPO42–) (or phosphate; e.g., osteoblasts of bones or yolk proteins).
- It is the mitochondria’s job to keep the suitable concentration of calcium ions in the various compartments of the cell.
- The mitochondria are also involved in the formation of certain components of blood as well as hormones such as testosterone and estrogen.
- Ammonia detoxification enzymes are found in the mitochondria of the liver cell.
Matrix
It is a viscous or gel-like fluid that consists of a mixture of enzymes, ribosomes, inorganic ions, mitochondrial, nucleotide coagulation factors, and organic molecules. It is involved in the process of cellular respiration as well as the generation of ATP molecules in the body.
Cristae
Cristae is a term used to refer to the inner layer of the mitochondrial matrix that is surrounded by folds in the mitochondrial matrix. In addition to increasing the surface area of the inner membrane.
Ribosomes
The mitochondrial ribosome, also known as the mitoribosome, is a type of ribosome that is found within the mitochondria. It is a protein complex that performs its function by interpreting mitochondrial mRNAs encrypted in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
Inner membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins and performs its function by allowing only specific molecules to enter and exit the cell. As a result, they are also referred to as “special membrane transporters” (SMT).
Outer membrane
Porins are proteins found in the outermost layer of mitochondria that act as channels, allowing proteins to move freely between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondrial cell. It also contains a large number of enzymes that perform a wide range of functions.
Intermembrane Space membranes.
The space between the inner and outer membranes is referred to as the interstitial space. Each of the two sub compartments, the intercristal space and the lumen, is subdivided into a separate compartment. The cristae junctions, which are tubular structures ranging from 10 to 40nm in diameter, are what separate the two.
Conclusion
Endosymbiotic and autogenous origins of mitochondria are the two hypotheses that have been advanced in recent years. In accordance with this hypothesis, mitochondria were initially prokaryotic cells, involved in executing oxidative processes that were not entirely feasible for eukaryotic cells; they then evolved into endosymbionts that lived inside the eukaryote and shared its metabolic processes. Autogenous mitochondria, according to the autogenous hypothesis, were formed by a component of DNA from the nucleoplasm of the eukaryotic cell at the period of deviation with the prokaryotes; this DNA component would’ve been embedded by membranes, which prevented proteins from crossing it. As a result of the fact that mitochondria share many characteristics with bacteria, the endosymbiotic hypothesis is more broadly acknowledged.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



