The cytoplasm is a rich, semifluid liquid found in the cells of organisms that are closed off by the cell membrane. The cytosol, cytoplasmic structures, mitochondria, and other organelles are all found in the cytoplasm. Some sources consider the nucleus, a conspicuous organelle floating in the cellular fluid, to be part of the cytoplasm. As a result, in this situation, it would be the biggest organelle in the cytoplasm. However, this viewpoint considers cytoplasm to be a synonym for protoplasm. The protoplasm is the cell’s fluid life component, which is composed mostly of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. The protoplasmic contents between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope are referred to as the cytoplasm.
What is Cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is the viscous liquid that fills each cell and is surrounded by the cell membrane. The majority of it is composed of water, minerals, and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm includes all of the material both within and outside the nucleus. All of the organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria are also contained in cytoplasm.
The cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that is not occupied by organelles. The cytoplasm, despite its appearance of being devoid of structure or order, is really extraordinarily structured. The cytoskeleton is a network of protein scaffolding that gives the cytoplasm and cell structure.
Cytoplasmic Function
- The cytoplasm is the source of the majority of the cell’s enzymatic processes and metabolic activities.
- The cytoplasm is the space within the cell where the cell expands and grows.
- The cytoplasm acts as a suspension medium for the organelles.
- The cytoplasm serves as a buffer, protecting the cell’s genetic material as well as the cellular organelles from damage caused by movement and collision with other cells.
- Glycolysis kicks off cellular respiration in the cytoplasm. This process generates the intermediates that the mitochondria need to produce ATP.
- The majority of mRNA translation into proteins on ribosomes also takes place in the cytoplasm.
- The monomers that go on to form the cytoskeleton are also found in the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is essential for cells with particular shapes, in addition to being required for typical cell activity.
- The cytoplasm also helps to create order inside the cell by directing organelles to certain regions. For example, the nucleus is often found towards the centre of the cell, with a centrosome adjacent.
- Cytoplasmic streaming is necessary for putting chloroplasts near to the plasma membrane in order to enhance photosynthesis and for transferring nutrients throughout the cell.
- Cytoplasmic streaming is thought to have a role in the creation of cellular subcompartments as well as organelle location in some cells, such as mouse oocytes.
- Cytoplasmic Inheritance: The cytoplasm is home to two organelles, the chloroplast and the mitochondria, each of which has its own genome. These organelles are inherited directly from the mother via the oocyte and hence represent genes inherited outside the nucleus. These organelles reproduce independently of the nucleus and respond to cell requirements.
Structure of Cytoplasm
Cell organs are made up of diverse structures that exist within cells. Each component is unique and has a certain purpose. Cells are made up of three major components: the cell membrane, the cytoplasm, and the nucleus.
The cell membrane, commonly known as the plasma membrane, is a bi-lipid membrane layer that divides the cell organs from their environment as well as other cells. The exterior shield of a cell that protects all of the nucleus and cytoplasm.
The nucleus, which is one of the largest organelles in the cell, comes next. They were given independent authority of a cell. The last organelle in the cytoplasm contains a jelly-like substance in which all of the cell organelles are positioned.
It is a very essential component of the cell. It has a jelly-like texture and connects the cell membrane and nucleus. The cytoplasm is embedded in every cell, and it houses several cell organs such as the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, and so on.
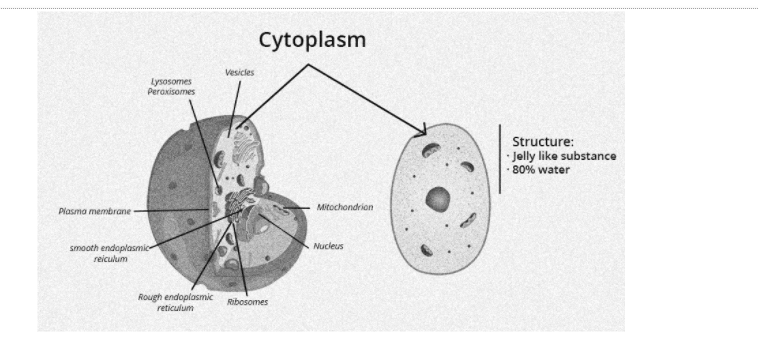
It is easily visible under a microscope using the staining approach. This is the region within a cell where several biological processes take place. In this area of the cell, the cell’s metabolism is at its peak.
The cytoplasm’s physical properties vary. There is sometimes rapid diffusion across the cell, causing the cytoplasm to resemble a colloidal solution. At times, it appears to take on the characteristics of a gel-like or glass-like material. It is believed to have the features of both viscous and elastic materials, being capable of deforming slowly under external force while also recovering its previous shape with minimum energy loss. The cytoplasm near the plasma membrane is also’stiffer,’ whereas the portions in the interior resemble free flowing liquids.
The cytoplasm is separated into three parts:
- The cytoskeleton and its associated motor proteins
- Organelles and other massive multi-protein complexes
- Cytoplasmic inclusions and dissolved solutes are present.
Cytoplasm Properties
- The cytoplasm is typically white and composed of 70% – 80% water.
- It contains Proteins, carbohydrates, salts, sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides
- The cytoplasm is made up of dissolved nutrients as well as waste materials.
- The cytoplasm’s exterior transparent and glassy layer is known as the ectoplasm or cell cortex, while the inner granular mass is known as the endoplasm.
- The plasmogel is a thick, jelly-like material that surrounds the cytoplasm. The plasmosol is the surrounding region of the nuclear zone, which is thin and liquid in nature.
Conclusion
Cytoplasm is the viscous liquid that fills each cell and is surrounded by the cell membrane. The cytoplasm is a rich, semifluid liquid found in the cells of organisms that are closed off by the cell membrane. The protoplasm is the cell’s fluid life component, which is composed mostly of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. The protoplasmic contents between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope are referred to as the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm includes all of the material both within and outside the nucleus. The cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm that is not occupied by organelles.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



