Plastids are a distinctive feature of plant cells. They synthesise and store food in algal and plant cells. All plastids begin as proplastids and mature into a variety of specialised mature plastids depending on the function of the cell. Mature plastids can even transition between different forms.
Plant cells have three distinct kinds of plastids:
- Chloroplast: This organelle contains chlorophyll and carotenoids and is responsible for photosynthesis.
- Chromoplast: Carotene and xanthophylls are found in the chromoplast. They colour flowers and fruits and aid in pollination and seed dissemination.
- Leucoplast: They are colourless and store a variety of food ingredients, such as amyloplasts, proteinoplasts, or aleuroplasts, and elaioplasts.
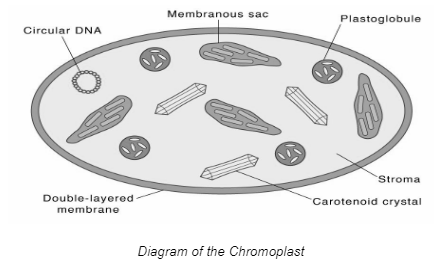
Chromoplast
These are pigment-producing and pigment-storing plastids. Carotene and xanthophylls are found in them. Chromoplasts are the pigments that give leaves, fruits, flowers, and vegetables their hues. They produce hues other than green. These are found in flowers and ripe fruits. Additionally, chromoplasts aid in the pollination and dissemination of seeds.
Characteristics of Chromoplasts
- Chromoplasts are carotenoids-containing plastids.
- They lack chlorophyll yet produce a variety of other colours.
- Carotenoid pigments are responsible for the yellow, orange, and red hues found in fruits, flowers, old leaves, and roots, among other things.
- Chromoplasts can arise from chloroplasts that are green. Chlorophyll and thylakoid membranes degrade and carotenoids accumulate, for example, during fruit ripening.
- During fruit ripening, the change of chloroplasts to chromoplasts is quite visible. Carotenoids are synthesised in large quantities. As a result, chlorophyll and thylakoids are oxidised.
- While plastid DNA stays unaltered after transformation, ribosomes and rRNA are lost.
- Certain chromoplasts are capable of reverting to chloroplasts, for example, the chromoplasts of carrot root and citrus fruit, pumpkin, and cucumber. They lose their carotene pigment and acquire chlorophyll and a thylakoid system.
- Gibberellin and nitrates induce redifferentiation to chloroplasts.
- In plants such as pepper and tomato, chromoplast formation is irreversible.
- Chromoplasts are generated from proplastids or leucoplasts in various plants such as papaya, carrot, mango, and watermelon.
- Light, temperature, and nutrients all play a role in chromoplast production.
- They include plastoglobules and carotenoid-lipoprotein substructures that are responsible for storing particular carotenoid pigments and lipoprotein fibrils.
- Carotenoids are classified as carotene and xanthophylls. Carotene is an orange pigment, while xanthophyll is a yellow pigment.
- Xanthophylls, such as fucoxanthin, lutein, and others, contain oxygen.
- Carotenoids, such as carotene and lycopene, are composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen.
Structure and classification
Chromoplasts can be separated and categorised into four distinct varieties using a light microscope. The first kind is formed of granulated proteic stroma. The second is made up of protein crystals and granules of amorphous pigment. The third kind is made up of crystals of protein and pigment. The fourth form is a chromoplast composed entirely of crystals. An electron microscope provides more details, allowing the identification of substructures such as globules, crystals, membranes, fibrils, and tubules. The substructures of chromoplasts are absent from the mature plastid from which they separated.
Types of Chromoplasts
Essentially, chromoplasts are heterogeneous plastids. They are categorised into four categories based on their carotenoid content:
- Globular Chromoplasts: These are composed of carotenoid-containing plastoglobuli. They are frequently localised in the plant cell’s peripheral stroma. For instance, Ranunculus repens has petals, Capsicum has yellow fruits, and Citrus fruit has a perianth.
- Membranous Chromoplasts: Around twenty concentric membranes contain carotene pigments. Citrus sinensis–petals, daffodils, and tulips
- Tubular Chromoplasts: Carotenoids are found in the tubules of lipoproteins. Capsicum, hypanthium, and rose all have red fruits.
- Crystalline Chromoplasts: Carotene is incorporated as crystals in these chromoplasts. Carrot roots contain beta-carotene, whereas tomato fruits contain lycopene.
Functions of Chromoplast
- They are critical for cross-pollination and seed dissemination by attracting animals and insects.
- In plants, carotenoids act as antioxidants.
- Carotene is a precursor to vitamin A found in carrots.
- Carotenoids in the diet can minimise the risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
- Fucoxanthin has been demonstrated to have anti-diabetic and anti-obesity properties.
- In certain plants and algae, chromoplasts function as organelles within the cells that house the photosynthesis machinery.
Conclusion
Plastids are required for a wide variety of typical plant cell processes and so come in a variety of forms. Plastids are classified by their colour, shape, and ultrastructure (Whatley 1978; Miller 2005; Wise 2007). The chloroplast is a photosynthetic plastid so named because of its green colour. Non-photosynthetic plastids can be generically classified according to their pigmentation into leucoplasts, which are ‘white’ or colourless plastids, and chromoplasts, which are coloured plastids known for their accumulation of carotenoids. Amyloplasts, elaioplasts, etioplasts, and proplastids are all types of leucoplasts.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




