A cell is the smallest fundamental unit of life, and it is responsible for the survival of the living being. Cells are known as the building blocks of human life.
Robert Hooke was the first biologist who discovered the cell in 1665. When he observed a piece of bottle cork under a microscope, he noticed minuscule structures, and he named those structures cells. Cells differ, but they share some common organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, lysosome, plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, vesicle, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes cytoskeleton.
Types of cells based on their structure
Prokaryotic cells: Prokaryotic cells are without a nucleus and have a nucleoid region where the genetic material is freely suspended. This cell ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 µm in size. Reproduction in these cells is asexual and generally by the process of binary fission.
Eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and range between 10-100 µm in diameter. The plasma membrane works as a security guard, maintains nutrients’ transport, and is responsible for cell-to-cell communication. Reproduction is done sexually as well as asexually. Some common examples are plants, fungi, protozoans, and animals. Plant cell contains chloroplast and other plastids in them.
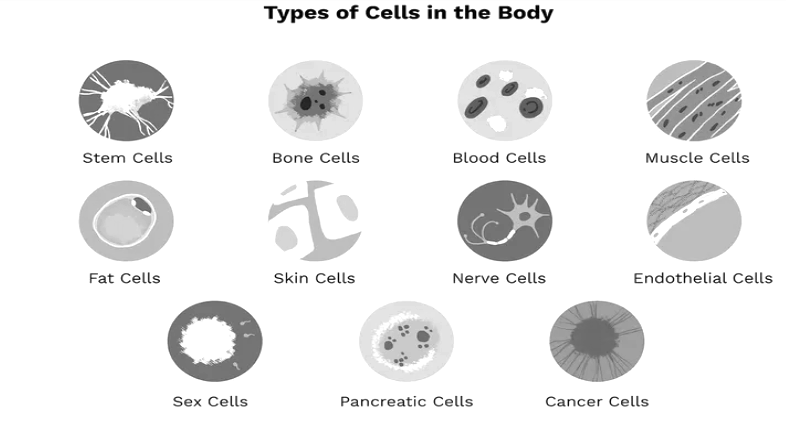
Types of cells
Refer to the cell types diagram to better understand the cell types and their structure.
Stem cells: Stem cells are found in the embryo and adult tissues such as bone marrow. These cells originate as unspecialised cells. They can develop themselves as specialised cells while others can play the role of building blocks of specific organs and tissues. Stem cells can divide and replicate many times to repair the tissues.
Endothelial cells: These cells form a single cell layer lining all blood vessels. Signals from endothelial cells organise the growth and development of connective tissue cells. They regulate exchanges between the bloodstream and the surrounding tissues.
Bone cells: In general, there are three types of bone cells:
- Osteoclast that dissolves bone—Osteoclasts do the work of decomposing for resorption and assimilation while healing
- Osteoblast that forms new bone—They regulate mineralisation and produce organic substance osteoid
- Osteocytes are surrounded by bone and communicate with other bone cells, they are also helpful in the formation of bone and maintaining calcium balance
Blood cells: Blood cells originate from the bone marrow. There are three types of blood cells:
- Red blood cells: Red blood cells determine the blood type and transport the oxygen to the heart
- White blood cells: White blood cells are the immunity builder cells that destroy pathogens
- Platelets: Platelets help clot the blood and prevent excessive blood loss when the blood vessels are damaged due to external or internal reasons
Muscle cells: There are three types of muscle cells.
- Skeletal muscles attach to bones and help involuntary movements. These are covered by protective connective tissues that support muscle fibre bundles.
- Cardiac muscle cells, found in the heart, form involuntary muscle. These do not require conscious efforts to operate. They also help in heartbeat synchronisation and heart contraction.
- Smooth muscle, not striated like cardiac and skeletal muscle, is the muscle that lines body cavities. It forms the protective walls of many body organs such as the kidney, intestine, etc.
Fat cells: Fat cells are also known as adipocytes, and they are the main constituent in the adipose tissue. Fat cells are a storehouse of the stored fat known as triglycerides used for energy. These cells are round and swollen when fat is stored, shrinking when fat is utilised for energy. They also have hormones that help in regulating blood pressure, blood clotting, and cell signalling.
Skin cells: Skin cells or epithelial tissues are the building block of skin. A layer of connective tissues supports them called the dermis and an underlying subcutaneous layer. These cells help protect the internal structure of the body from damage. Moreover, they guard the body against germs, prevent dehydration, store fat and produce vitamins and hormones.
Nerve cells: The fundamental unit of the nervous system is a neuron. Neurons are known as nerve cells. They act as a messenger among the brain, spinal cord, and other body organs through nerve impulses. A neuron consists of a cell body, and nerve processes are finger-like structures (axons and dendrites) that transmit signals.
Pancreatic cells: Pancreatic glands function as exocrine and endocrine organs. It releases hormones through ducts as well as directly into other organs. The main functions of pancreatic cells are regulating blood glucose levels digestion of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. These cells are found in small clusters known as islets of Langerhans. Insulin, glucagon, and gastrin are the common hormones these cells produce.
Cancer cells: Cancer cells are opposite to other cells and function to destroy the body. These cells originate from mutation stemming from radiation and ultraviolet light. These cells develop decreased sensitivity to anti-growth signals.
Reproductive or sex cells: Reproductive cells bring new life into existence. Male reproductive cells called gametes or sperms have a tail called flagella. Female reproductive cells or ova are large in comparison to male reproductive cells. Generally, body cells are replicated by mitosis, but gametes are reproduced by mitosis.
What cell types undergo mitosis?
Except for the reproduction cells (sperm and female egg cells), most of the cells in the body divide by mitosis. The parent cell breaks apart into two daughter cells. This daughter cell has the chromosomes of the parent cell.
Conclusion
A cell, the smallest structural unit in a body, is the building block of all living beings. A human body has more than 30 trillion cells in a body. They are the artist of or energy making in a body from food. Although there are many cells in a living body, few types of cells are listed in science. For example, nerve cells, muscle cells, bone cells, blood cells, skin cells, etc.
Each category of cells has its responsibility and work to perform. Without proper functioning of cells in a human body, a healthy living lifestyle is impossible.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out