We consider flowers the eye-catching, attractive, bright and fragrant structures of plants. But if we look at it from a biological perspective, flowers are the major reproductive part of plants. Not only reproductive, but it is also a source of food for other organisms.
Complete or incomplete flowers
A complete flower comprises stamen (male), pistil (female), sepals, and petals. On the other hand, an incomplete flower may lack one or more aforementioned structures.
A flower that contains both male and female parts is called a hermaphrodite. Flowers that contain only the male parts are called staminate flowers, and flowers containing only the female part are called carpellate flowers.
Also, if both male and female flowers are borne on the same plant, it is called monoecious plant, and if they are borne on a different plant then it is called a dioecious plant.
Anatomy of a flower diagram
Learn the different reproductive parts of a mature flower with this anatomy of a flower diagram:
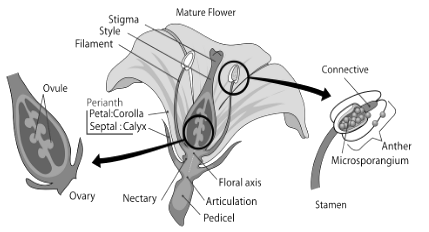
Image via Pixabay
Parts of flower
A flower can be divided into two major parts:
- Vegetative parts: these parts are not directly involved in reproduction. These are petals and sepals.
- Reproductive parts: just as the name suggests, these parts are directly involved in reproduction. It includes stamen (male) and pistil (female) reproductive parts.
Vegetative part
Petals: Petals are generally the bright coloured attractive part of a flower. The colour, shape and number of petals vary from plant to plant. A group of petals form a corolla. The bright colour of corolla attracts insects and bees for nectar, which helps in pollination.
Sepals: Below the petals, there is a green coloured part called sepals. The main function of sepals is to protect the flower in the bud stage. Number of sepals also varies in different plants. Sepal units together are called calyx.
Reproductive part
A flower may contain both or either male or female parts. The reproductive part involves the following:
Male reproductive part
Stamens: The male part of a flower is called the stamen. It is also called androecium. It consists of three parts, i.e., anther, filament and connective tissue.
Anther: Anther is a sac-like structure generally yellow in colour. The main function of an anther is producing and storing the pollen.
Filament- Filament is a long threadlike structure that holds and supports the anther. Connective tissue connects anther to the filament.
Detailed structure of pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance packed inside the pollen sacs of a flower called the anther. Pollen is light and sticky. The pollen grain contains cytoplasm with a pollen tube and a sperm nucleus.
Female reproductive part
Pistil: pistil is the innermost female part of the flower called gynoecium. The pistil consists of three parts, i.e., the stigma, style and ovary.
Stigma: It is the topmost and sticky part of the gynoecium, which receives pollen grain.
Style: it is a long, cylindrical part of the gynoecium which connects the stigma to the ovary. Pollen grains fall over the stigma and travel through style to reach the ovary.
Ovary: it is present at the base of the gynoecium. It contains ovules. An ovary is a place where seed formation occurs.
Detailed structure of the ovary
The ovary contains a chamber-like structure called locules. These locules contain ovules, which further transform into seeds. These ovules are attached to the anterior wall of the ovary called the placentae.
There is an outgrowth of the placenta in some plants called the obturator. This obturator guides the pollen tube to the micropyle.
When pollen sticks to the stigma, it passes through the style and reaches the ovary, fertilising with ovules and becoming the seed. The ovary then turns into a fruit. So we can say the fruit is a ripened ovary.
Besides this, all these four parts of a flower, i.e. sepals, petals, stamen and pistil, are arranged into a whorl, attached to the receptacle, and further attached to the stem called a peduncle.
What is pollination
Pollination is the process of pollen transportation from anther to stigma. The pollination can occur through different means such as insect pollination, bird pollination, wind pollination, etc.
Function of flower
These are some primary functions of a flower:
- The primary function of flowers is reproduction by producing seeds.
- Flowers produce nectar for certain birds and insects, which helps in pollination.
- Finally, a flower’s ripened ovary turns into fruit that acts as food for other living organisms, including humans.
Conclusion
A flower is a bright-coloured, fragrant and attractive part of a plant. It is composed of petals, sepals, stamen and carpels, where stamen and carpels are the male and female reproductive part of the plant, respectively. Flower is the major reproductive part of any plant bearing it. The pollen grain (male) travels through the style and reaches the ovary, where it fertilises the ovules and forms a seed. The ripened ovary becomes a fruit that other organisms, including humans, consume.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




