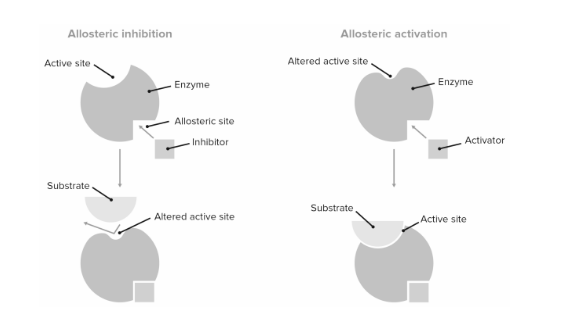
The allosteric site allows substances to turn on or off enzyme activity by activating or inhibiting it. These chemicals bind to the allosteric site and alter the enzyme’s conformation, or shape. Allosteric inhibitors are molecules that turn enzymes off. Allosteric inhibitors modify the geometry of the active site, preventing it from binding to the substrate. The enzyme won’t be able to complete its work if it can’t bind to the substrate! These molecules, as well as the allosteric site to which they bind, act as the enzyme’s ‘off switch.’ Allosteric activators, on the other hand, improve the efficiency of the enzyme. They alter the structure of the enzyme in the same way that allosteric inhibitors do, but they improve the enzyme’s ability to bind the substrate rather than making it worse. This improves the enzyme’s performance. These compounds and their allosteric sites act as the enzyme’s ‘on switch.’
Allosteric Modulation :
In biochemistry and pharmacology, allosteric modulation is used to change the activity of molecules and enzymes. A common drug, for example, is designed to bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing the binding of a substrate to that enzyme, resulting in a decrease in enzyme activity. When an effector binds to an enzyme’s allosteric site (also known as a regulatory site) and changes the enzyme’s activity, this is known as allosteric modulation.
Allosteric modulators are designed to fit the allosteric site of an enzyme to create a conformational change in the enzyme, specifically a change in the shape of the active site, which results in a change in the enzyme’s activity. Modulators, unlike most medicines, are not competitive inhibitors. They can be either positive (activating) or negative (inhibiting), generating a rise in enzyme activity or a decrease in enzyme activity. Allosteric modulation allows for the control of the effects of certain enzyme activities, which makes allosteric modulators extremely useful in pharmacology. [10] Allosteric modulation can be difficult to discern from substrate-presented modulation in a biological system.
Types of Allosteric Sites:
Homotropic : A homotropic allosteric modulator is both a substrate and a regulator of the activity of its target enzyme. It usually works as an enzyme activator. O2, for example, is a haemoglobin homotropic allosteric modulator.
Heterotropic: A heterotropic allosteric modulator is a regulatory substance that isn’t also a substrate for the enzyme. It could be either an enzyme activator or inhibitor. Hemoglobin is modulated by heterotropic allosteric modulators such as H+, CO2, and 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Other Activators : Some allosteric activators are referred to as “essential” or “obligate” activators because their action on their target enzyme is very low or non-existent without them, as is the case with N-activity acetylglutamate on carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I.
Allosteric Regulation :
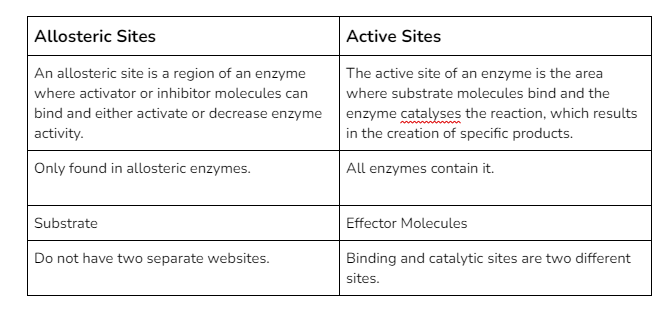
In general, allosteric regulation refers to any type of regulation in which the regulatory molecule (either an activator or an inhibitor) binds to an enzyme in a location other than the active site. The allosteric site is the location where the regulator binds.
Comparison of Allosteric Sites and Active Sites :
Conclusion :
Enzymatic reactions in cells are closely regulated, allowing important processes to happen while blocking unneeded or harmful ones. Allosteric regulation is one method of controlling enzyme activity. The covalent modification or noncovalent binding of a regulator to an enzyme can cause an enzyme to change shape and expose an active site in allosteric control. Negative regulation can also work in this way, with the active site being obscured.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



