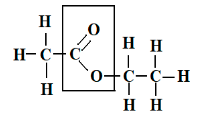
Ester
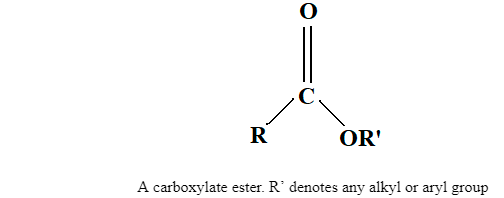
Ester has a fruity odor. It is an organic chemical compound in which the carboxylic functional group is present. By the reaction of an acid with an alcohol, an ester is formed. From carboxylic acid, an ester is derived, and it is most common. Ester can be represented by the formula RCOOR’. As in the substitution reaction of an alcohol and carboxylic acid at least a –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O- alkyl group.
Ether
Ether is an organic chemical compound that is highly volatile in nature. Ethers have a relatively low boiling point because ether molecules fail to form hydrogen bonds with each other. Lower ether acts as an anesthetic and there is no flavor present in simple ether. The dipoles C-O do not cancel each other and the bond angle of C-O-C is around 110°, therefore ether is slightly polar.

Ester and Ether
Ester is characterised by a carbon bond to three other atoms: a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to s carbon, and a single bond to oxygen. Ester is also known as a functional group that is commonly found in organic chemistry. At the carbonyl, carbon ester reacts with nucleophiles. The carbonyl is attacked by strong nucleophiles though it is weakly electrophilic. The key feature of an ester is that they have -COO- a group which is known as a functional group somewhere in the middle of the molecule as –
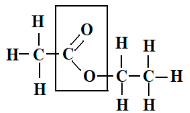
A -COO- functional group of ester, ethyl ethanoate.
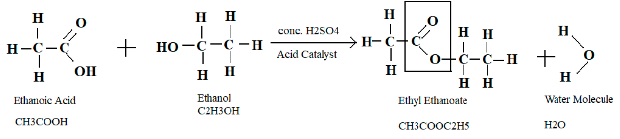
One distinctive feature of an ester is they have a sweet or fruity smell. Ester evaporates easily as they are volatile in nature. Esters are commonly used in food beverages, perfumes, etc. To make an ester one needs to use carboxylic acid and alcohol. For example, ethyl ethanoate is made up of ethanoic acid, and ethanol and acid catalyst (conc. H2SO4) is needed to be used. Therefore the equation will look like this –
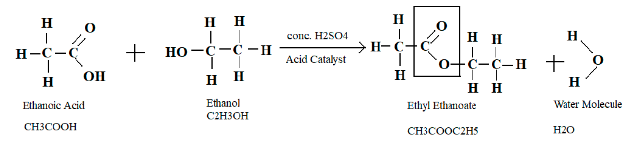
The ester group -COO- can also be called an ester link.
Whereas, -O- is the functional group of ether. Ether contains an oxygen atom that is attached to two hydrocarbon groups. Diethyl ether (C4H10O) is a compound that is used as an early anesthetic. -O- is a functional isomer of alcohol. Since ether can be obtained by the elimination of water from two molecules of alcohol, they are also known as anhydrate of alcohol. Like –
Ethers are represented by a general formula
R and R’ are the alkyl groups or aryl groups. Ethers are of two types-
Symmetrical ethers (General formula R – O- R) – Example: CH3 – O – CH3 (methoxy methane)
and Unsymmetrical ether (general formula R – O – R’) – Example: CH3 – O – CH3 (methoxy ethane)
Differences between Ester and Ether in tabular form are
|
SL. No. |
Ester |
Ether |
|
1 |
The functional group of an ester is -COO- |
The functional group of ether is -O- |
|
2 |
Oxygen and carbon atoms are linked with a double bond. |
Oxygen and carbon atom is linked with a single bond. |
|
3 |
Ester can polarise easily due to the carbonyl group. |
Ether is unpolarized because it does not have a carbonyl group. |
|
4 |
Ester does not have symmetrical structures due to the carbonyl group. |
If both alkyl groups on either side of the oxygen atom in an ether group are similar then ether can have a symmetrical structure. |
|
5 |
Esters are derived from a carboxylic acid. |
Ethers are derived from alcohol. |
|
6 |
Example of ester: Ethyl propanoate. |
Example of ether: Pentabromodiphenyl ether. |
Conclusion
It is to conclude that Ester has a fruity odor. It is an organic chemical compound in which the carboxylic functional group is present. -O- is the functional group of ether. Ether contains an oxygen atom that is attached to two hydrocarbon groups.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out