Introduction
Wien’s Law or Wien’s Displacement Law statement is that at distinct temperatures, the black body radiation curve is different at each wavelength. In simple words, the black body radiation curve at 3000K will be different from the one at 6000K. The wavelength at which the black body emits maximum radiation would also be different at different temperatures. This relation between the temperature and wavelength of emitted radiation is described by Wien’s Displacement Law formula. It is crucial to understand the concept of a black body, to grasp this law and the mathematics behind it.Black Body
A black body is an ideal body that absorbs radiation of all wavelengths. It does not reflect or transmit any light falling on it. For comparison, a metal surface absorbs only 6% of the incident radiation, reflecting or transmitting the rest. An ideal black body would absorb 100% of it. It emits black body radiation. Every physical body wants to maintain equilibrium. So a black body also wants to maintain thermal equilibrium. For this reason, it emits and absorbs radiation at the same rate. The radiation emission is governed by Planck’s Law. This means that temperature alone determines its emission spectrum. At thermal equilibrium, a black body emits either the same or more thermal radiation than any other body at a given temperature and frequency. A good example of a black body can be a box with a small hole on top whose interior walls are painted black in colour. Any radiation that is incident on it can find no way out and hence gets fully absorbed. When it is at thermal equilibrium, then it will emit as much radiation as any other body will at thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 1. Emissivity is defined as the ability or measure of a body to emit energy in the form of thermal radiation. Any body which is not black body would have emissivity less than 1.Wien’s Displacement Law Statement
Now that we understand black body, let’s understand Wien’s Law. It defines the relationship between the temperature of a black body and the wavelength at which maximum radiation is emitted. It has been found that the two have an inverse relation, i.e., lower is the temperature, higher is the wavelength at which the maximum radiation is emitted, and vice versa. The law was given by a German scientist named Wilhelm Wien, for which he was also rewarded with a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1911. He was working on this experiment in the 1890s. He used an oven with a small hole as a black body as close as possible to ideality. He performed certain experiments that helped him establish the relation between temperature and wavelength of the emitted radiation. He observed that the black body does not emit radiation uniformly over all wavelengths, but there’s one wavelength at which maximum radiation is emitted.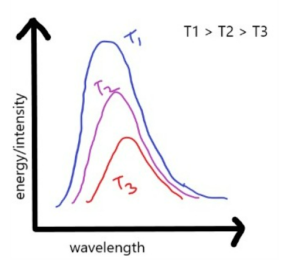 As can be seen from the above figure, as the temperature increases, the wavelength at which the maximum radiation is emitted keeps decreasing.
As can be seen from the above figure, as the temperature increases, the wavelength at which the maximum radiation is emitted keeps decreasing.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






