Suppose an individual is driving a car and unhurriedly he begins to coalesce it into the freeway. Here, he tends to drive faster and promptly increases the speed of the car. So, this upswing in the speed of the object over time is related to acceleration. It is due to the event of acceleration that a body or an object integrates itself with the surroundings around it.
Another example of this can be the instance when a person is taking off on a thoroughfare trip and driving at a speed of 50km/h. To match the momentum with other automobiles, the person increases his car’s speed to 70 km/h. So, here we refer to the individual’s vehicle as moving in acceleration. Notably, the Système International (SI) unit of this vector quantity (acceleration) is m/s². That means when an object has a change in velocity as m/s and the time duration as 1 second, then the acceleration of the object is 1 m/s². Thus, the SI unit of acceleration is conveyed as m/s ².
Define Acceleration
Acceleration pertains to the alteration in the velocity of an object over time. Here, an alteration in velocity can either be a transition in the speed of the object or the orientation in which the object is taking off in motion, or both. In broad terms, we can define acceleration as the speeding of the object, where there can be a change in the speed or the direction, or both in certain cases, irrespective of the fact if it’s up or down.
If there is an increase in the speed of the body in motion, then it is referred to as positive acceleration. Nonetheless, on the other hand, if the object is reducing its speed then the momentum which is present in the body is known as the negative acceleration. In the words of Newton, it is the net unbalanced force acting on the object which makes it accelerate in the direction it wishes for.
Example of acceleration
We can take an instance of a car that is at rest and moves in a uniform motion with a speed of 20 m/s in a time duration of 4 seconds. So, Is the car accelerating or not? If yes, what will be the rate of acceleration?
Yes, the car is accelerating because we know that by the fact there is a transition in the speed of the car over some time period from 0 to 20 m/s. Now, we are knowledgeable of the process that entails a change in velocity.
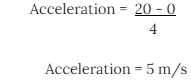
Acceleration Unit
SI unit of acceleration
The Système International (SI) unit of this vector quantity (acceleration) is m/s². That means when an object has a change in velocity as m/s and the time duration as 1 second, then the acceleration of the object is 1 m/s².
Feet per second square
The above unit comes under the system of foot-pound-second where if the body alters its velocity with the difference of 1 ft/s between the initial and current velocity in a time period of 1 second, then the acceleration of the body is pertained to be 1 m/s².
Gal unit of acceleration
This unit of measurement is named after prominent scientist Galileo Galilei who was the first one to research gravity caused acceleration. As the basis goes by, the gravitational acceleration is incited due to the force of gravity on our planet, earth and other celestial bodies of the universe. If related with the SI unit of acceleration i.e. m/s ², then 1 gal is equal to 0.01 m/s ².
Standard gravity (g)
Standard gravity is caused due to the gravitational force of the Earth. Standard Acceleration affected by earth’s gravity is equivalent to 9.8 m/s ². The other name for Standard gravity is g force. However, one shouldn’t confuse this term g force with the basic definition or concept of force. Standard acceleration due to gravity is not identical to the idea of acceleration due to gravity. Both of them have different significance and are affected by different events.
Planck Acceleration (ap)
Named after a famous personality, Max Planck, the change in the velocity that happens from the initial point to the speed of the light is referred to as the Planck acceleration.
Conclusion
Acceleration pertains to a change in the momentum of an object within a given period. As a vector quantity, acceleration implicates both transitions in the speed and the direction of the object that is in motion. If either of the conditions of motion by the object is contented then the object is said to be in acceleration. Acceleration is sometimes perplexed with speeding up of the object only. Regardless, if the object is speeding down, the body in motion would still be referred to as being in acceleration. Thus, one shouldn’t perplex acceleration with positive acceleration only, it can also be related to negative acceleration as well.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






