In chemistry, a chemical bond is a strong interaction that exists between two or more atoms. The bond holds the atoms together and gives them a strong enough attraction to each other to allow them to be separated. This separation is also known as diffusion, and the atoms can then be moved around, or changed into different chemical compounds.
The bond between the atoms is what gives a substance its chemical properties.The strength of a material, the ability to resist breaking, is determined by its chemical bonds. These bonds are what hold the molecules of a material together, and determine the strength and hardness of a material. Specifically, the strength of a material is determined by the number of covalent bonds it contains, the strength of these bonds, and the distance between them. The more covalent bonds a material contains, the stronger it is.
Chemical bonding and its types
Chemicals can bond together to form molecules. When two or more substances mix, they can react with each other and form new chemical compounds. Chemical bonds are of four types: ionic, covalent, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals. Ionic chemical bonds are strongest between dissimilar substances and are held together by ions.
Let’s discuss all the four types of chemical bonds
Ionic bond: Ionic bonds are the strongest bonds in nature, and are formed when two ions are joined together. Ionic bonds are formed when a metal ion donates a pair of electrons to a non-metal ion, creating a shared electron pair between the two ions. These bonds are so strong because they are very compact and have a high degree of covalent bonding.An ionic bond is a chemical bond that forms when atoms transfer electrons to one another. Ionic bonds are found in salts, which are compounds composed of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). For example, in sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium ions transfer one electron to chloride ions, creating sodium cations and chloride anions. Ionic bonds are very strong, they are hard, and brittle.
Covalent bond: Covalent bonds are the strongest bonds in nature, and are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Covalent bonds are formed when an atom donates a pair of electrons to a neutral third atom, forming a shared pair of electrons between the three atoms. These bonds are very flexible and have a high degree of ionic bonding. Covalent bonds are more commonly seen in non-metals and are generally polar.They are the glue that holds together molecules and the framework that holds together our cells and tissues. Covalent bonds are also the cause of some of our most painful diseases, including cancer. Covalent bonds are the backbone of our world.
Hydrogen bond: Hydrogen bonds are the attractive forces that hold molecules together in water, and in other polar solvents. They can occur between molecules that have either a partial or complete positive or negative charge, or between molecules and a water molecule. In polar solvents, they are the main force that keeps solids and liquids together. In nonpolar solvents, such as benzene, they are not very important.
van der Waals interactions:The van der Waals forces are the weakest of the quantum forces; they are long-range, fluid-like forces that cause molecules to stick together. The forces are named after the physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, who discovered them in the year 1860s. Van der Waals forces are also known as colloidal forces, or simply colloids. They are the forces that cause molecules to stick together, much like the forces that cause magnets to stick together.
Electronic theory of chemical bonding
In accordance with this theory, which was proposed independently by Kossel & Lewis, a chemical bond is formed between atoms in order to get the nearest inert gas configuration. Which can be achieved by either losing electrons or gaining electrons or by sharing electrons
We can understand the structure and behaviour of atoms and molecules by using the theory of chemical bonding. This theory is an electronic theory, which means that it tries to explain chemical bonding in terms of the motions of the electrons within the atoms and molecules. The theory of chemical bonding makes predictions about how the structure of molecules and the properties of materials are related to the way the electrons are arranged within them. The theory of chemical bonding has been a remarkably successful scientific theory and has enabled us to make a wide range of predictions about the world and to develop technologies such as drugs, plastics, and solar cells.
Octet Rule
Kössel and Lewis in 1916 made an important theory of chemical integration among the atoms known as the electronic theory of chemical reactions. According to this, atoms can combine or by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another (gain or loss) or by sharing valence electrons to have an octet in them valence shells. This is known as octet law.
Examples:
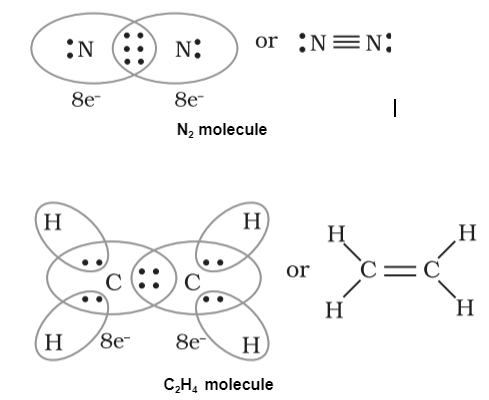
Conclusion
The molecules and compounds that make up our world are held together by chemical bonds. The stronger the bonds, the stronger the material. But not all bonds are equal. Some are stronger than others, and some are stronger in certain circumstances than others.
There are four types of chemical bonds: ionic bond, covalent bond, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals. We have also discussed the electronic theory of chemical bonding in which a chemical bond is formed between atoms in order to get the nearest inert gas configuration. This can be achieved by either losing or gaining or sharing electrons.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






