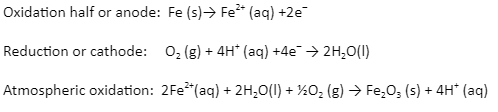Corrosion of metals is an electrochemical phenomenon. It takes place when a refined metal is converted to a more stable form like its oxide, hydroxide, or sulphide state which results in the deterioration of the material. A redox reaction takes place during corrosion.
Corrosion slightly coats the surface of the metal with oxides or other metal salts. Metal rust, silver corrosion, the development of green copper and copper cover are some examples of rust. It causes extensive damage to buildings, bridges, ships and all other metals, especially metal.
A huge amount of money is lost every year on account of corrosion. In corrosion, a metal is oxidised by the loss of electrons to oxygen, resulting in the formation of oxides. Corrosion of iron (commonly referred to as rusting) occurs in the presence of water and air. Below are the reactions for anode, cathode, and atmospheric oxidation:
Oxidation half or anode: Fe (s)→ Fe2+ (aq) +2e–
Reduction or cathode: O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) +4e– → 2H2O(l)
Atmospheric oxidation: 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H2O(l) + ½O2 (g) → Fe2O3 (s) + 4H+ (aq)
Ways to Prevent Corrosion
1. By Painting
Paints can hold up erosion by modifying the anodic reaction. For this to happen, the colour of the paint must be either metallic, elemental, or solvable. In general, paint flicks defend by virtue of their high electrolytic resistance. They readily acquire charge and are fairly impermeable to ions.
2. By Applying Grease or Oil
Oil lubricates metal parts, allows them to manoeuvre with less friction, and forms a protective barrier against rust. The principle here is simple; with a coating of oil, moisture cannot react with the iron within the metal and cause rust.
3. By Galvanization
The process of depositing a thin level of zinc metal on iron is called galvanisation. The galvanisation process involves applying a zinc coating to the face of ferrous material to slacken or defend from the erosion of the substrate metal. A zinc coating produces a physical hedge while also working as a sacrificial anode. When zinc reacts with atmospheric oxygen, oxide is produced, resulting in the formation of zinc hydroxide. This process takes place in the presence of humidity. The zinc hydroxide further reacts with dioxide within the natural terrain, leading to a skinny subcaste of impermeable zinc carbonate, which binds to the zinc beneath. Zinc carbonate protects and preserves the zinc subcaste from further sharp oxidation. This process is the same as the formation of a passive oxide layer of aluminium, that protects an aluminium substrate from further oxidation.
4. By Tin Plating and Chromium Plating
Coatings like electrolytic nickel, electroless nickel, or tin or chromium can provide strong corrosion resistance, but this only happens if the deposit thickness is sufficient to improve the seamless surface of the metal substrate. This is because nickel or tin protects the metal by closing the surface in the atmosphere. This is because nickel or tin is less effective (nobler) than base metal – called cathodic coating.
5. By Alloying
Alloying prevents rust by combining several essences, or rudiments that interact with one another, to produce a defensive subcaste over the loftiest of the face of the essence. This hedge limits oxygen and air from getting past the face of the essence and piercing the inner structure. Any ferrous material that doesn’t hold other reactive metals that form this level is subject to rust.
6. Sacrificial Coatings
Sacrificial coating is placing another metal on top of the original surface metal so there’s more chance of that metal corroding than the one beneath it. There are two methods to achieve sacrificial coating – cathodic protection and anodic protection.
Conclusion
Corrosion of metals is an electrochemical phenomenon. Corrosion takes place when a refined metal is converted to a more stable form like its oxide, hydroxide, or sulphide state. Corrosion results from a redox reaction. It slowly coats the surfaces of metallic objects with oxides or other salts of the metal. A large amount of money is lost every year due to the corrosion of metals. However, there are a few ways to prevent the occurence of this phenomenon. Some of them are painting, galvanization, tin plating, alloying, chromium plating, and sacrificial coatings.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out