Did you know that the Earth’s atmosphere is divided into several layers? Each layer has its own unique set of characteristics, and it is important to understand these layers if you want to learn more about our planet’s atmosphere. In this blog post, we will discuss the Structure of the Atmosphere in detail. We will talk about what each layer is made up of, and what its functions are. So if you’re interested in learning more about our planet’s atmosphere, stay tuned!
What is the structure of the atmosphere?
The atmosphere is made up of different layers, each with its temperature and air pressure. The Earth’s atmosphere is divided into five main layers: the thermosphere, the exosphere, the mesosphere the troposphere and the stratosphere,
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from the surface to an altitude of about 12 kilometres (about seven miles). This is where nearly all of the weather and clouds occur. The temperature in the troposphere generally decreases with height. It is the layer responsible for our weather.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from an altitude of about 12 kilometres (about seven miles) to an altitude of 50 kilometres (about 31 miles). The temperature in the stratosphere generally increases with height. This is because there is very little mixing in this layer and the sun’s ultraviolet radiation heats it. The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which absorbs some of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the third layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from an altitude of 50 kilometres (about 31 miles) to an altitude of 80 kilometres (about 50 miles). The temperature in the mesosphere generally decreases with height. This is because there is very little mixing in this layer.
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the fourth and final layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from an altitude of 80 kilometres (about 50 miles) to an altitude of 600 kilometres (about 372 miles). The temperature in the thermosphere generally increases with height. This is because there is very little mixing in this layer and the sun’s ultraviolet radiation heats it. The thermosphere is sometimes divided into two layers: the lower thermosphere and the upper thermosphere.
Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from an altitude of about 600 kilometres (about 372 miles) to an altitude of about 20,000 kilometres (about 12,427 miles). The exosphere is where most of the satellite’s orbit is. The temperature in the exosphere generally decreases with height. This is because there is very little mixing in this layer and the sun’s ultraviolet radiation heats it.
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is a region of Earth’s atmosphere that extends from an altitude of about 50 kilometres (about 31 miles) to an altitude of about 1000 kilometres (about 620 miles). The ionosphere is divided into three layers: the D layer, the E layer, and the F layer. The ionosphere is important because it reflects radio waves and helps us communicate with each other.
The Hottest layer of Atmosphere
The thermosphere is the hottest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from about 90 km to 600 km above the planet’s surface. The air in this layer is so thin that the molecules do not collide often. Instead, they are free to zip around at high speeds. At these high altitudes, the air is heated by ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. This makes the thermosphere the hottest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, even though it is also the farthest from the Sun.
The Coldest layer of the earth
The atmosphere is made up of several layers, each with its unique characteristics. The layer closest to Earth’s surface is the troposphere. This is where we live, and it experiences a wide range of temperatures. The air is warmer near the ground, where the Sun’s heat is absorbed, and cooler at higher altitudes. The air in the troposphere can get as cold as -93°C!
Conclusion
Atmospheric pressure is created by the weight of the atmosphere. The higher the altitude, the lower the atmospheric pressure. This pressure difference can cause problems for aircraft and create dangerous weather conditions. The structure of the atmosphere is constantly changing and evolving. It is important to study the atmosphere to better understand our planet and how it works. What is the Structure of Earth’s Atmosphere?” was originally published on The Structure of Atmosphere. Students need to be aware of these dangers and how to stay safe when travelling in high-pressure environments. By understanding atmospheric pressure, students can take precautions to stay safe while enjoying their travels.
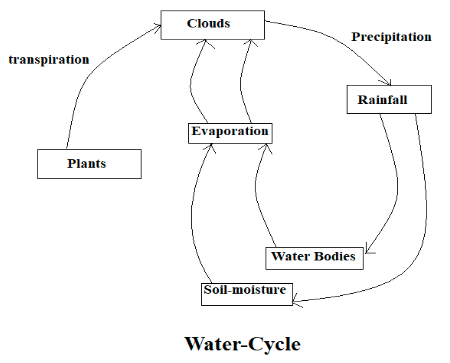
Water Cycle
Due to the heat of the sun water evaporates from lakes, seas, rivers, and other water bodies; this process is known as evaporation, water also evaporates from the plant’s leaves, which is known as transpiration. As the water rises from lakes, seas, rivers, and other water bodies in the atmosphere, it gets cool and condenses to form clouds as a continuous process of evaporation and condensation, gradually the clouds get heavy, and as a result, precipitation occurs in the form of rain. And this rainwater is stored in any of the following reservoirs such as the ocean, soils, glaciers, under the Earth’s surface as groundwater, lakes, snowfields, etc.
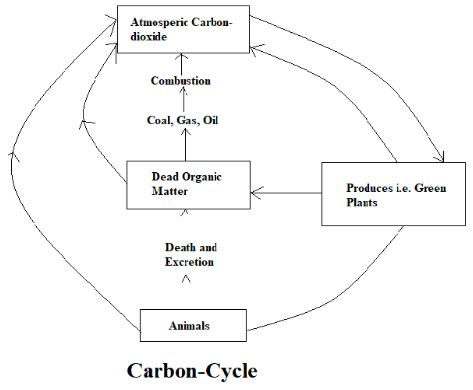
Carbon-Cycle
The carbon concentration in the atmosphere is about 0.03%. Circulation of carbon from the atmosphere to the biosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and returns to the atmosphere is known as the carbon cycle. The carbon from the atmosphere enters into the plants through photosynthesis for synthesizing food particles, when the plants are consumed by terrestrial organisms, carbon dioxide enters them. When these terrestrial organisms die the carbon dioxide enters the soil. Carbon dioxide enters into the water as carbonates, which helps the aquatic plants to perform photosynthesis. CO2 returns to the atmosphere from fossil fuel, from respiration of animals, the release of smoke from vehicles, from the burning of wood. If CO2 increases in the atmosphere it disturbs the natural carbon cycle.
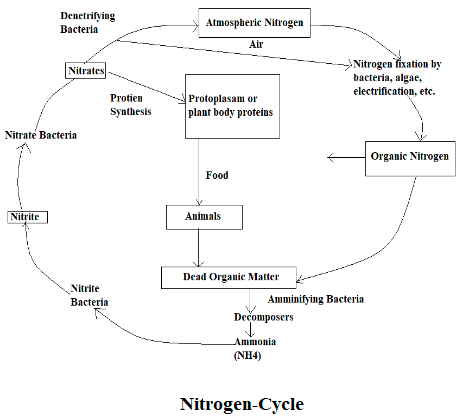
Nitrogen Cycle
The atmosphere is made up of 78% Nitrogen; we need nitrogen for DNA and proteins. Nitrogen that is available in the atmosphere cannot be directly consumed by plants, they can consume the nitrogen when it is fixed i.e. when combined with other elements like carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. By the action of denitrifying bacteria, nitrogen is spontaneously entering into the air and through the action of electrification and lightning, nitrogen is entering into the soil.
Conclusion
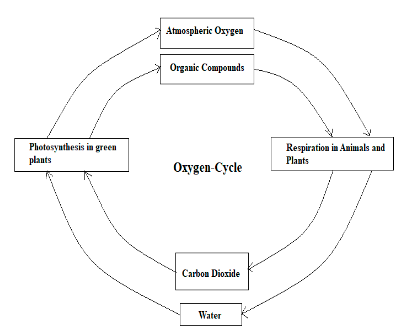
It is to conclude that the biochemical cycle in an ecosystem is defined as the transformation and transport of chemicals in ecosystems. In wetlands, by unique hydrological conditions, biogeochemical cycles are strongly influenced. There are four main important biogeochemical cycles in the ecosystem are oxygen cycle, water cycle or hydrologic, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




