pH Meter can be defined as a scientific instrument that is used to measure the hydrogen-ion activity in solutions thus indicating its alkalinity and acidity as pH value. Its accuracy ranges from ± 0.1 pH to ± 0. 001. One needs to attain knowledge about the pH meter as it appears to be very useful in many situations, especially in chemical laboratory analyses.
Body:
The working mechanism of pH Meter and pH meter principle:
The basic pH meter principles are given below
A solution that contains a greater number of H⁺ ions will be acidic in nature.
A solution that contains a greater number of OH⁻ ions will be alkaline in nature.
Range of pH value → 1 – 14.
A solution that possesses a pH value = 1, will be highly acidic whereas,
A solution that possesses a pH value = 14, will be basic in nature.
A solution’s acidity or alkalinity nature depends on the hydrogen ions (H⁺) concentration as well as the concentration of hydroxyl ions (OH⁻).
Neutral Solution → pH 7 (Pure Water).
Glass pH container contains as shown in the figure below:
Two Electrodes.
Single Sensor Electrode.
A Reference Electrode.
The above electrodes are in a glass tube form that contains:
(I) a pH 7 buffer.
(II) A saturated solution of potassium chloride (KCL).
The components in a Sensor electrode bulb are;
- A glass of porous nature.
- silica and metallic salts coated a glass membrane that is permeable.
Along with a silver wire which is coated with silver chloride (AgCl) immersed in pH 7 buffer in the bulb, another silver wire being coated with silver chloride is immersed in saturated potassium chloride (KCl ) solution.
When the glass container is kept in a solution for pH measuring, hydrogen ions(H+) start accumulating near the bulb which replaces the bulb’s metal ions. Electric flow is generated by the interchange of ions that is caught by the silver wire.
The pH meter measures the energy of the electric flow generated as above by changing it into a pH value by contrasting the generated energy with the electrode reference.
The solution’s increasing acidity contains a higher hydrogen ions concentration which shoots up the voltage. Thus, the increasing voltage results in a decrease in the reading of pH in the pH meter.
Increasing alkalinity leads to the decrease of the hydrogen ions or increasing hydroxyl ions concentration decreases the energy and thus increases the value of pH in the pH meter.
pH Meter Diagram:
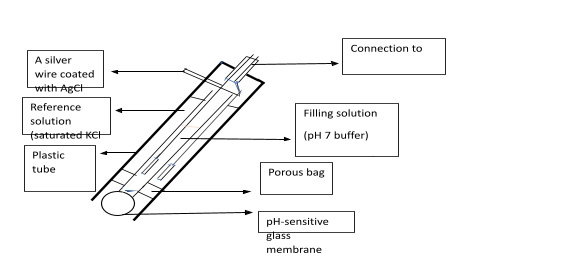
The above pH meter diagram represents the various components of a pH meter.
We need to have a fair idea about its basic components.
How to operate a pH meter?
The very first step will be turning on the pH meter by switching it on. After turning it on, the ATC indicator along with the MEAS annunciator will make an appearance on the LCD.
Electrodes are to be thoroughly washed with water that is distilled.
The sample temperature needs to be maintained at 25 ° C.
Then, the electrodes are to be immersed in the specimen and stirred to create a specimen that is homogenous. We need to make sure that the point of the electrode is completely dipped in the sample.
Keep patience till the reading is stablised.
Once the reading is stable, there will be an activation of an indicator saying ‘READY’. The reading is frizzed by pressing the key that says HOLD and then saving it.
Advantages of pH meter:
- Calibration of pH is cheap as well as robust.
- User-friendly pocket-sized meters.
- The results are accurate and highly reliable.
Disadvantages of pH meter:
- The output results or readings are affected by the heat generated.
- The glass electrodes being used while pH calibration needs to be thoroughly washed to prevent it from influencing the readings further.
Precautions to be maintained while handling a pH meter:
Handle the electrode with absolute responsibility as it may break due to small negligence.
The electrode is to be kept immersed inside the solution that the company directs or in a neutral solution of KCl (3M-4M)
Maintain the level of the inner fluid beyond the measured solution.
The electrodes need to be cleaned immediately after experimenting or else it would sustain the substances which can accumulate or stick to the glass bubble.
Do not immerse the electrodes in solvents that can dissolve glass, particularly solvents such as hydrofluoric acid or other concentrated Alkalis.
Avoid rubbing or wiping the electrode bulb.
Applications of pH meter:
Agricultural industries – Measures the pH of soil.
Checks the quality of water for municipal water supplies or swimming pools.
Chemical & Pharmaceutical industries – Measures the pH value of solutions.
Food industry – Used in the case of dairy products like cheese, yogurt, etc.
Helps in making the detergents.
pH meter price:
pH meter’s price varies according to their types. Let’s discuss them:
Pen Testers:
- Pocket-sized instruments.
- Cheaper rates.
- Designed with pH meter, LCD, and electrode all in one.
- Very mobile.
- Used in hydroponics, food manufacturing, pool, or spa maintenance industries.
- Price – ₹480 – ₹ 900 (in India)
Handheld Meters:
- Slightly larger than pen testers.
- Electrodes separate from the meter.
- Used in the field of aquaculture, agriculture, and water treatment.
- Price – ₹1000 – ₹ 4000(in India)
Benchtop pH meters:
- One of the largest pH meters.
- Featured as desk or wall-mounted.
- Possesses a high degree of accuracy.
- Suitable for laboratory and other professional use.
- Used in food processing industries as well as quality assurance industries.
- Price – ₹5000 and above.
Conclusion:
The pH meter serves great usage in food processing industries, chemical laboratories in the form of detergent powder, and many others as well as widely in the agricultural sector. It helps to control the availability of various nutrients in soil or water, microbial and other biological activities, and also chemical behaviors in laboratories.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






