Fluid is defined as continuously deformed or flowing material under applied shear stress regardless of the pressure applied. All the analysis regarding fluid and its application is termed as fluid mechanics. Fluid mechanics helps to analyze the characteristic behavior of fluids in different forces and atmospheres. It has different significance in the field of chemical and mechanical engineering. In order to explain the fluid properties, it is important to understand the concept of fluid mechanics. The concept of fluid properties also deals with mass density, viscosity, and the specific weight of the material. Apart from this, there are some other properties also discussed under fluid properties.
What are Fluid properties?
There are several concepts regarding fluid properties that are used in engineering and geosciences areas. However, the fundamental concept for fluid properties that are common in every area is density, temperature, and composition. Volume and mass are broad properties that depend on the amount of material. Apart from this temperature, density and pressure refer to the fluid’s intensive properties.
This whole discussion derived from the concept of fluid mechanics. There are three aspects that are significant in fluid mechanics: fluid statics, fluid kinematics, and fluid dynamics.
Fluid statics: the type of fluid that is not moving is called static fluid; hence, the study is termed fluid statics.
Fluid kinematics: this study refers to the study of those fluids that are in a motion state. Here the effect of external pressure is not considered.
Fluid dynamics: this study considers the motion fluid in all conditions of external pressures affecting the movement of the fluid.
Properties of fluid
We can categorize the fluid properties into three sections. Kinematic properties include the determination of the fluid motion. This also includes acceleration and velocity. Physical properties of fluid cover a wide area where the study discusses the physical state or condition of the fluid.
Density: it is generally defined as the “ratio of fluid mass and volume of the fluid”. Density is dependent on the temperature and external pressure. It can be defined as “=mass of fluid/volume of fluid”, where stands for density.
Weight density: Weight is defined by the weight possessed by every unit of fluid. Therefore gravity is also influenced by weight acceleration. This can be also defined as “=weight/volume” where stands for a specific weight.
Bulk modulus: It refers to the ability of the fluid to prevent any changes in the volume at the time of being exposed to external factors. It is the opposite of compressibility. It can be defined as K= (dP/d), where K is a numerical constant. The proposed formula for dimension is “[M1L-1T-2].”
Viscosity: It refers to the capability of the fluid to prevent its flow on the surface. Viscosity generally happens in the fluid due to “molecular momentum transfer”. The viscosity formula is “= (du/dy)”.
Compressibility: Compressibility is the opposite stage of bulk modulus where the fluid can decrease the size and volume when external pressure is applied. The simplest formula for compressibility is “=1/K”, where stands for compressibility.
Types of fluid mechanics
There are several types of fluid mechanics, also known as fluid flow. These are: “ideal fluid”, “ real fluid”, “Newtonian fluid”, “non-Newtonian” and “ideal plastic fluid”.
Ideal fluid: This kind of fluid does not have viscosity and cannot be compressed. An imaginary fluid does not have any practical existence.

Real fluid: This kind of fluid has a viscosity effect.
Example: Air, water, petrol.
Newtonian fluid: this kind of fluid follows “Newton’s law of viscosity”. Hence it is named Newtonian fluid.
Example: Gasoline, motor oil and water.
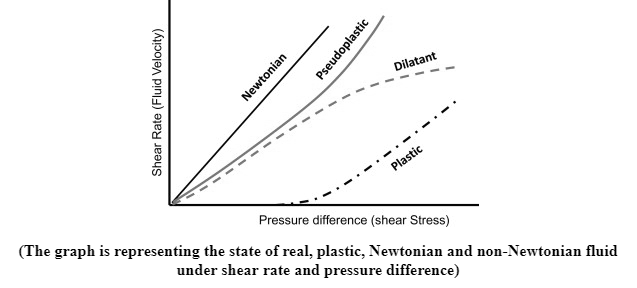
Non-Newtonian fluid: It is the opposite of the Newtonian fluid, it does not follow “Newton’s law of viscosity”.
Example: Tooth paste, corn starch, shampoo, blood and many more.
Ideal plastic fluid: A fluid whose “shear stress value” is more than the value of yield is known as an ideal plastic fluid. Here the shear stress is proportional to the velocity gradient.
Example: Toothpaste is categorized as ideal plastic fluid.
Application of fluid mechanics
Some common applications of fluid mechanics are in the hydroelectric power plants in form of water to generate electricity, in hydraulic machines in form of water and oil to provide the capacity to the machines for lifting heavyweights. Fluids are also used in the automobile sector as a lubricator, power generator, and as cooling agent for the engines. Fluid is also used here as refrigerants to absorb the heat. Fluids are also essential in the “nuclear power plant” as a coolant and fluid. These are some versatile uses of fluid mechanisms in different operational areas.
Importance of fluid mechanics in mechanical engineering
Fluid mechanics, properties of fluid is an important aspect in mechanical engineering subjects. Proper understanding of fluid mechanics and properties of fluid helps to prepare the design of various engines, such as steam engines and turbines. In addition, what are the specific roles of the fluid in different machines and operating functions? Thus, fluid mechanics and mechanical engineering are anticipated from each other.
Conclusion
Fluid is a very simple and common thing in daily life, but it has various dimensions and versatile use in different application areas. Thus a proper understanding of the fluid mechanics is important to analyze the particular characteristics of the fluid property before applying. Also determining the changing nature of the fluids property is also important.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




