Gauss and Green’s theorem is a topic that is covered in volume and surface integrals. Gauss theorem’s most common form is the Gauss divergence theorem. The most interesting fact about the Gauss theorem is that it can be represented by using index notations.
Gauss and Green’s theorem has a very easy formula known as the Euler expression for the conservation of mass and it is 0 in the smooth case. And after some time, this formula came to be known as the divergence theorem, which was discovered by Lagrange 2 in 1762.
This is a very interesting topic, and here we will learn this in detail.
Gauss and Green’s Theorem
Gauss and Green’s theorem states that the electric field net flux in a closed figure is always equal to the total amount of charge enclosed by the surface and will undergo division through the permittivity of the medium.
Gauss and Green’s theorem is mainly used in a line integral when it is around a closed plane curve C, and it is a double integral over the part or region which is enclosed by C.
This theorem is really helpful as it helps to solve the line integrals into more simple double integrals and convert them into the more simple line integrals.
The formula of Gauss and Green’s theorem is:
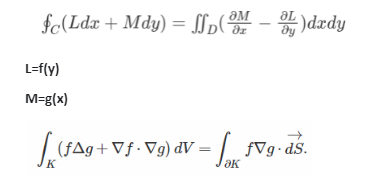
S = Surface element
K = flux of vector field through boundary
f = 1 + x. *e( y + z )
g = x2 + y2 + z2
V = Line integral
Gauss and Green’s theorem relationship with the divergence theorem:
When we take two-dimensional vector fields, the Green theorem is always equal to the two-dimensional divergence theorem. Where delta x F is the divergence on the two-dimensional vector field F, n is recognized as an outward-pointing unit normal vector on the boundary.
Green’s Gauss Example
Let’s learn Green’s Gauss Example for better understanding.
Solve ∫cy³dx-x³ dy
c = circle of radius 2.
P= y3, Q = – x3
A=πr2
dA=2πrdr
Implementing Green’s and Gauss theorem,
∫cy³dx – x³dy = ∫∫D -3x² – 3y2d A
Using polar coordinates:
∫cy³dx – x³dy = – 3∫∫D (x² + y2) dA
= – 3∫02π ∫02 r3 drdθ
= – 3∫02π (r4/4)|0 2 dr dθ
= – 3∫02π 4dθ
= – 24π
Condition for Gauss and Green’s theorem
Gauss and Green’s theorem is applicable to only those curves that are oriented counterclockwise. But if you want to apply this theorem on the clockwise curve, you can also do that, but you have to flip the sign first for the same part unless you cannot apply Gauss and Green’s theorem.
So the most often asked question is, can Gauss and Green’s theorem only be negative?
It’s totally up to you whether you are traveling clockwise or anticlockwise. You will apply the green theorem only when the curve is positive. If you get the answer using the Gauss Green theorem, it will always be negative.
Gauss and Green’s theorem can never be used in single dimensions. It will always be used in two dimensions.
Where does the Green theorem apply?
Green theorem only works when the curve is closed; otherwise, it will never work. If someone is thinking of applying it on the open curve, don’t even think about it. This theorem is not made for things like them.
The main work of the green theorem is that it will convert the line integral into the double integral to make the circulation continue.
Gauss and Green’s theorem is a very important topic. It is a topic from the volume and surface integrals needed to be studied. There are a number of ways in which we can use Gauss and Green’s theorem in our everyday life and in maths too.
Continuity Equations
Continuity expression gives more examples about differential and integral forms, which are related to each other by the term called divergence. This continuity equation states that the divergence of conserved quantity is equal to the sources of that quantity.
It is an interesting fact that any inverse law can be written in the form of Gauss law. There are two examples that follow the Gauss law, Coulomb’s law and the Gauss law of gravity.
Conclusion
After reading all this, you now know how and where to use Gauss and Green’s Theorem. The thing which should be kept in mind is that Gauss and Green’s theorem is only applicable to the double integral closed surfaces. It is a very complicated yet very easy topic.
If you want to learn this topic well, you have to perform various examples. Practicing examples will help you clear your concept, and you will know this topic well.
The most common mistake done by the students is that they think after reading once, there is no need to reread this or to practice any questions and skip this part.
So to not end up in this problem, practice the questions now and clear your topic now itself.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




