What is FMR?
- A bilateral agreement between India and Myanmar.
- Allows tribal residents along the India-Myanmar border to travel 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
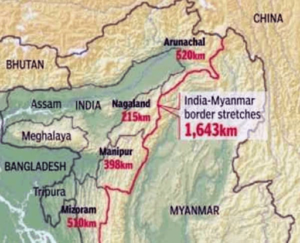
- India shares a 1,643 km-long border with Myanmar, traversing Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram.
- Initiated in the 1970s and last revised in 2016.
- Aimed at fostering people-to-people connections due to strong ethnic and familial ties across the border.
- Eligibility: Citizens of India or Myanmar with a border pass, valid for a year, allowing stays up to 2 weeks per visit.
Challenges and Suspension:
- The 2021 military coup in Myanmar led to an influx of undocumented migrants into Mizoram and Manipur.
- Migrants mainly from the Kuki-Chin-Zo ethnic group, sharing ties with communities in Mizoram and Manipur.
- Manipur suspended FMR in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and has urged the central government to permanently end it, citing ethnic violence.
End of FMR and Implementation of Smart Fencing:
- The Indian government plans to implement an advanced smart fencing system along the entire India-Myanmar border.
- The project, expected to complete in 4.5 years, will replace the FMR and introduce visa requirements.
- The move aims to curb the misuse of FMR by insurgent groups for attacks, and to control illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and gold smuggling.
Why in News:
- The Union Government has decided that it would be scrapping the Free Movement Regime with Myanmar soon.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






