Introduction:
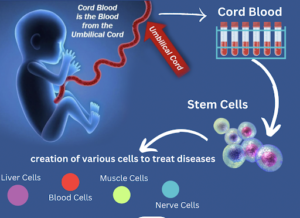
- Cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth. It is a rich source of stem cells.
- Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to divide for indefinite periods and differentiate into specialized cell types of the body.
- Regenerative medicine leverages these stem cells to repair or replace damaged cells and tissues.
Regenerative medicine deals with the process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues, or organs to restore or establish normal function. |
Key Points:
- Cord blood is a non-invasive and ethically suitable source such as stem cells.
- These stem cells can be used in the treatment of over 80 diseases, including blood disorders, immune deficiencies, and certain types of cancer.
- Cord blood banking ensures a perfect genetic match for the donor, eliminating the risk of immune rejection in transplants.
Why in News:
- Recently, new research is extending the utility of cord blood in treating neurological conditions like cerebral palsy and autism.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






