Aspect | Full-Reserve Banking | Fractional-Reserve Banking |
Basic idea | Safeguarding the Deposits | Expanding Credit and Risk |
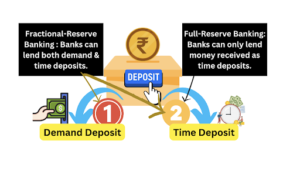
Demand Deposit Handling | Banks must hold 100% of demand deposits in vaults; act as custodians | Banks can lend out a portion of demand deposits. |
Fees for Deposit Service | Banks charge fees for safeguarding deposits. | No fees are usually charged for deposit safeguarding. |
Lending Source | Banks can only lend money received as time deposits. | Banks can lend more money than they hold in cash. |
Risk of Bank Run | Low risk of bank runs due to full reserves. | Higher risk of bank runs if many demand cash at once. |
Handling Crises | Usually, no need for central bank intervention in crises. | Central banks can provide emergency cash if needed. |
Economic Perspective | Supporters argue it prevents crises and stabilizes the economy. | Supporters argue it spurs investment and growth. |
India follows the Fractional Reserve Banking System. |
Bank Run:
|
Why in news?
- Recently there have been debates regarding Full-Reserve Banking (100% reserve banking) versus Fractional-Reserve Banking.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






