A surface integral is a surface integration extension of multiple integrals. It can be thought of as the line integral’s double integral equivalent.
Surface integrals are used if you want to combine a group of variables connected with points on a surface. the two dimensional equivalent of line integrals. You may also think of it as a means to apply double integrals to curved surfaces.
The Riemannian sum corresponding to a surface integral divides the surface into little squares (or other shapes) and adds their values, whereas the volume integral divides the body into small cubes (or other 3-dimensional shapes) and adds their values.
The surface integral of a vector field across a closed surface, known as the flux through the surface, is equal to the volume integral of the divergence over the region inside the surface, according to the divergence theorem.
Surface Integral
A surface integral is a generalization of multiple integrals to integration over surfaces in mathematics, particularly multivariable calculus. It can be thought of as the line integral double integral equivalent. A scalar field (that is, a function of position that returns a scalar as a value) or a vector field can be integrated over a surface (that is, a function which returns a vector as value).
Surface
A two-dimensional point locus that is either flat or curvy (such as the boundary of a three-dimensional region).
Surface refers to outside or surface traits, as well as transporting anything by land or sea. The texture of a table’s top is an example of surface. A person who looks to be honest but is not is an example of surface. Surface mail, for example, is delivered by truck rather than by plane.
A two-dimensional point collection (flat surface), a three-dimensional point collection with a curved cross section (curved surface), or the boundary of any three-dimensional solid. Surface is a continuous boundary that divides a three-dimensional space into two sections in general.
The total surface area of a solid is equal to the sum of the areas of all of its faces or surfaces. The tops and bottoms (bases) as well as the remaining surfaces make up the faces. The surface area of a solid without the bases is called the lateral surface area.
Direction of the vector
The orientation of a vector is the angle it makes with the x-axis, which is its direction. A vector is created by drawing a line with an arrow at one end and a fixed point at the other. The vector’s direction is determined by the direction in which the arrowhead is pointed.
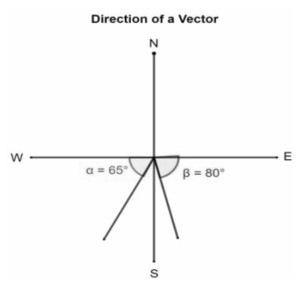
The angle a vector makes with the x-axis is its direction. A vector is a line with an arrow at one end and a fixed point at the other. The vector’s direction is determined by the arrowhead’s orientation.
The slope of a line is connected to the direction of a vector formula. The slope of a line passing through the origin and a point (x,y)is known asx/y. We also know that if this line makes an angle of, then its slope is tan, i.e. tan=xy as a result, =tan-1y / x.Thus, the direction of a vector(x,y) is calculated using the formulatan-1(y / x), but the quadrant in which (x,y) is located should also be considered while computing this angle.
Steps to find the direction of a vectorx,y:
- Find using α= y / x.
Find the direction of the vector using the following rules depending on which quadrant (x,y) lies in:
| Quadrant in which(x,y) lies | θ (in degrees) |
| 1 | α |
| 2 | 180°-α |
| 3 | 180°+α |
| 4 | 360°-α |
To determine the direction of a vector whose ends are defined by the location vectors (x1,y1) and x2,y2, follow these steps:
- Find the vector (x,y) using the formulax, y=(x2–x1,y2–y1)
- Find and just as explained earlier
Important Notes on Direction of a Vector
- The angle formed by a vector’s tail with east, north, west, or south can be used to represent the vector’s direction
- We may use the appropriate formula for each quadrant after obtaining the value of |y / x|
- The angle formed by a vector in the counterclockwise direction from east can also be used to determine its direction
Surface Integral Example
An example of computing the surface integrals is given below:
Example:
Evaluate
∬sxyzdS
, in surface S which is a part of the plane where Z=1+2x+3y, which lies above the rectangle0,3×[0,2]
solution:
Given:
∬sxyzdS
, and z=1+2x+3y.

= 9² / √14
Therefore, the surface integral for the given function is
= 9² / √14
Conclusion
A surface integral is a multiple integral surface integration extension. It is the double integral’s counterpart to the line integral.
When you want to aggregate a group of variables associated to locations on a surface, you utilize surface integrals. Line integrals in two dimensions are equivalent. It can also be thought of as a way of applying double integrals to curved surfaces.
The volume integral splits the body into little cubes (or other 3-dimensional shapes) and adds their values, whereas the Riemannian sum corresponding to a surface integral divides the surface into little squares (or other shapes) and adds their values.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






