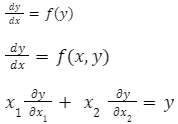Differential calculus is a branch of mathematics that studies the rates at which quantities change. It is one of calculus’ two traditional divisions, the other being integral calculus, which studies the area beneath a curve. The derivative of a function, related notions such as the differential, and their applications are the primary objects of study in differential calculus. The derivative of a function at a given input value describes the function’s rate of change near that input value.
In this article, we will learn more about differential calculus, its basics, Equations of Differential Calculus, and applications.
Differential Calculus
Differential calculus is the study of a dependent quantity’s rate of change in relation to a change in an independent quantity. The speed of a moving object.
For example, can be interpreted as the rate of change of distance with respect to time. If the function to be differentiated is y=f(x), then the differential calculus notation is f'(x) = dy / dx.
Differential Calculus Basics
The following are some key terms related to differential calculus:
Functions – A function is defined as a relation from a set of inputs to a set of outputs, where each input corresponds to exactly one output. f(x) represents the function.
Dependent variable – A dependent variable is one whose value is determined by an independent variable. The dependent variable is what is measured or evaluated in an experiment or mathematical equation.
Independent variable – A variable in an equation whose value can be freely chosen without regard for the values of other variables. In equations like y = 3x – 2, the independent variable is x. The variable y is not independent because it is determined by the value of x.
Range and domain – The domain of a function is the set of values that can be plugged into it. This set contains the x values in a function like f. (x). A function’s range is the set of values that the function can take. This is the set of values that the function returns after we enter an x value.
Limits – The concept of a limit can be used to define a derivative. A limit in differential calculus describes the value of a function as it approaches a specific input value.
Derivatives – Derivatives are used in differential calculus to find the rate of change of a function. If a tangent line is drawn to a point on a function’s graph, the slope of the tangent will give the function’s derivative at the point where the tangent touches the curve. A function’s derivative, f(x), is written as f'(x), dy /dx, and df/dx.
Continuity – In mathematics, continuity is a rigorous formulation of the intuitive concept of a function that varies without abrupt breaks or jumps. A function is a relationship in which each value of an independent variable, say x, corresponds to a value of a dependent variable, say y.
Equations of Differential Calculus
Differential calculus equations, also known as differential equations, are equations that connect functions to their derivatives. Ordinary differential equations and partial differential equations are the two main types of differential equations. An ordinary differential equation is one that has only one independent variable and one or more derivatives with respect to that variable. One or more independent variables and their partial derivatives make up a partial differential equation.
Differential equations have three general formulas. Here are some examples:
Differential calculus applications
Determining the rate of change of a quantity in relation to another
In the case of finding an increasing or decreasing function in a graph
To determine a curve’s maximum and minimum value
To calculate the approximate value of a small change in a quantity
Conclusion
In this article we conclude that Differential Calculus is concerned with the rate of change of a quantity in relation to others. Derivatives are frequently used to find the maxima and minima of a function. Differential equations are fundamental in describing natural phenomena and involve derivatives. Derivatives and their generalizations appear in many areas of mathematics, including complex analysis, functional analysis, differential geometry, measure theory, and abstract algebra.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out