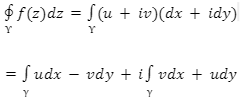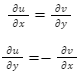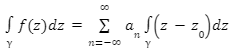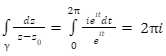Complex integration is the process of integrating a function of a complex variable along an open or closed curve in the plane of the complex variables. Complex integration includes Cauchy’s integral theorem. Complex integration is extremely valuable in engineering, physics, and mathematics.
We utilize this notion to determine the centre of mass, centre of gravity, and mass moment of inertia of vehicles, among other things. We use it to compute the velocity and trajectory of a satellite in its orbit.
We will look into Cauchy’s Integral Theorem, Cauchy formula optics, Cauchy’s residue theorem, and Cauchy formula refractive index in this article.
Cauchy’s Integral Theorem
The integral theorem of Cauchy is an element of complex integration. Cauchy’s integral formula is a fundamental statement in the field of mathematics known as complex analysis. It means that the values on the disc boundary dictate the complete holomorphic function specified on the disc. Integration formulas are provided for all derivatives of a holomorphic function.
Statement
If f(z) is analytic in a region R that is simply connected, then
Proof
For every totally enclosed closed contour gamma in R, write z as
z = x + iy
And f(z) as
f(z) = u + iv
Then gives
from Green’s theorem
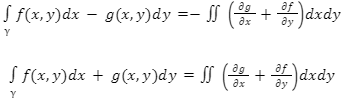
So,
![]()
The Cauchy-Riemann equations, on the other hand, require that this be done.
So,
Cauchy’s Residue Theorem
The residue theorem, often known as Cauchy’s residue theorem, is a useful tool in complex analysis for evaluating line integrals of analytic functions over closed curves; it can also be used to construct real integrals and infinite series. It extends and generalizes Cauchy’s integral theorem and integral formula. It can be viewed as a special example of the generalized Stokes’ theorem from a geometrical standpoint.
This is an important theorem in complex analysis, and it will allow us to make our prior ad hoc technique to computing integrals on contours that surround singularities more systematic.
Statement:
The Laurent series of an analytic function f(z) is given by
Employing a closed contour surrounding z0, can be integrated term by term
![]()
The first and last terms must vanish according to the Cauchy integral theorem, thus we have
The complex residue is denoted by a-1 Making use of the contour z = γ(t) = eit + z0 gives
as a result,
The theorem offers the general result if the contour γ contains several poles.
![]()
The collection of poles enclosed within the contour is denoted by A. The value of a contour integral for any contour in the complex plane thus depends only on the properties of a few very specific points inside the contour, according to this astonishing theorem.
Cauchy formula refractive index
Cauchy’s transmission equation is an empirical link between a transparent material’s refractive index and wavelength of light in optics.
It was called after Augustin-Louis Cauchy, a mathematician who defined it in 1837.
Cauchy’s formula in its most generic form is
where n denotes the refractive index, w denotes the wavelength, and A, B, C, and so on are coefficients that can be calculated for a material by fitting the equation to measured refractive indices at known wavelengths. The vacuum wavelength in micrometres is commonly used to express the coefficients.
In most cases, a two-term form of the formula suffices:
where A and B are coefficients that are unique to this form of the formula.
Conclusion
In this article we conclude that Complex integration includes Cauchy’s integral theorem. Complex integration is the process of integrating a function of a complex variable along an open or closed curve in the plane of the complex variables. The values of a holomorphic function inside a disc are determined by its values on the disk’s boundary, according to the Cauchy integral formula. The Cauchy integral formula has a lengthy history in complex analysis, combinatorics, discrete mathematics, and number theory, among other areas of mathematics. It was recently utilized to obtain an exact integral formula for the coefficients of cyclotomic and other polynomial classes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out