Once we learn simple mathematics like the basic operators, quadratic equations, squares, and cubes, we can learn complex chapters like the surds and logarithms. The questions based on logarithms are easy to solve once you learn how to use the logarithm table and know about the logarithm formulas.
Let’s learn what exactly are logarithms.
In simple terms, the logarithm is the concept that allows us to determine how many times a number is multiplied by itself to result in some other specific number. Logarithm topic helps assess the students’ natural instincts to deal with numbers.
Logarithm
The concept of logarithms:
- Logarithms are like squares, except in logarithms, there is no limit to how many times a number can be multiplied by itself.
- Logarithm helps us determine the number of times a number is multiplied by itself to get the other number as the product.
The number which is multiplied by itself is called the base. The number of times multiplication takes place is called the index of the logarithmic equation.
The general form of a logarithmic equation is as given below.
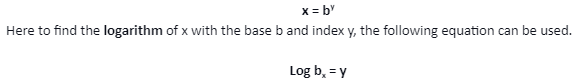
Here the condition is that x and b should be greater than 0, and b should not be equal to 1.
With the help of this formula, we can determine the following things.
- We can determine the base b if the index y and number x is given.
- We can determine the index y if the base b and index y is given.
Logarithm Table
The calculators have an operation to calculate the base and index of a logarithmic equation. However, in competitive exams like CLAT, the students need to solve these questions without any such help. In such cases, the logarithm table and the logarithm formulas are a great help.
To find the logarithm of a number with the help of the logarithm table, let’s get familiar with the concept of Characteristics and the mantissa part of the answer.
Characteristic Part:
The part of the number on the left side of the decimal point is called the characteristic part.
Any number greater than one has a positive characteristic.
For a number that is less than one, the characteristic part is negative.
Mantissa Part:
The part of the number to the right side of the decimal point is the mantissa part. A mantissa part is always a positive number. In case the mantissa value evaluates to a negative number, you should convert it into a positive number.
Follow the steps given below to find the logarithm of a number through the logarithm table.
- Step 1: Identify whether the base of the logarithm is ten or e and then pick the suitable log table.
- Step 2: Separate the characteristic part and the mantissa part of the given number.
- Step 3: First, use the common log table and then use the mean difference table.
- Step 4: Add the values obtained from the common log table and the mean difference table. That value is the mantissa part.
- Step 5: Now, find the characteristic part. For the numbers between 10 and 100, the characteristic part is 1.
- Step 6: Combine the characteristic part with the mantissa part to obtain the answer.
Logarithm formulas
There are six basic logarithm formulas to be used while solving any logarithm equations.
Let’s take a look at them.
Assume base b for all the equations,
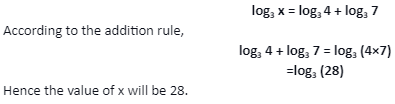
The product rule:
log(xy) = log(x) + log(y)
The product rule of logarithms states that the product of 2 numbers in the log can be simplified to the log of a first number plus the log of the second number.
The quotient rule:
log(x/y) = log(x) – log(y)
The quotient rule of the logarithms states that the division of 2 numbers in logarithms is equal to the log of the first number minus the log of the second number.
The log of power rule:
log (x y) = y × log (x)
The log of power rule of logarithms states that a log of a number raised to an exponential is equal to an exponential multiplied by the log of that number.
The log of e rule:
log(e) = 1
This rule is applied under the conditions that the logarithm is of the natural base.
The log of 1 rule:
log (1) = 0
The log value of 1 will always be equal to 0.
The log reciprocal rule:
log(1/x) = – log(x)
The reciprocal log rule states that the log of the reciprocal of any number will be equal to the negative of the log value of that number.
Such is the concept of the logarithm, logarithm table, and the logarithm formulas.
Conclusion
Logarithms are a useful tool in mathematics. Logarithms help us determine how many times a particular number has been multiplied by itself to obtain a particular product. The logarithms are of two types: Natural logarithms and common logarithms. The natural logarithms have the base e, and common logarithms have a base of 10.
We can find logarithms of numbers by using the log table. The first step is to identify the characteristic and mantissa of a number and then refer to the log table. There are six basic laws in the logarithms that help us solve the logarithmic equations.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out