In the year 1992 Panchayat Raj system was for the first time declared as the third level of India’s federal democracy by the Constitution of India through the 73rd Amendment Act. In the Indian subcontinent, the Panchayat Raj system was the oldest system of local government. The core meaning of the word Panchayat Raj is ‘panch’ which means five, ‘ayat’ means assembly and ‘raj’ means ‘rule’. The leader of every Panchayat is called Sarpanch or Mukhya, most elderly and understandable people in the village are chosen in this position. There are 6614 Block Panchayats, 630 Zila Panchayats, and 253163 Gram Panchayats in India as per the record of 2019.
Panchayati Raj System’s Power and Functions
Panchayat Raj system functions are the functions that all Panchayati Raj institutions perform; the functions which they perform are related to Panchayati Raj as specified in state laws. Panchayat Raj system functions are of two types; these are obligatory functions which means compulsory and the other one is an optional function, some states follow these functions of Gram Panchayat and the other states do not follow. The optional function may or may not be performed by the Panchayat, it depends on the resources a Panchayat is having. Such Panchayat Raj system functions are optional functions These are –
Setting up of breeding centres for cattle
Promotion of agriculture
Tree plantation on roadside
Organising child and maternity welfare
The obligatory or compulsory functions of the Panchayat Raj system functions are –
Primary healthcare
Constructing public wells
Public toilet and lavatories
Social health and primary and adult education
Minor irrigation
Vaccination
The supply of drinking water
Rural electrification
Cleaning of Public Roads
Sanitation
The scope of functions of Gram Panchayat was widened after the 73rd Amendment of the constitution. The programs that are expected to be performed by the Panchayats are –
Relief in natural calamities
Preparation of annual development plan for Panchayat area
Implementation and monitoring of poverty alleviation programs
Annual budget
Removal of encroachment on public lands
In some states, Gram Panchayat also performs the programs and activities like Gram Sabhas, non-conventional energy sources, biogas plants, public distribution system improved Chulhas, etc.
The legislature of the state provides power to the Gram Sabhas and the Panchayati Raj system has various responsibilities, powers, and functions. The Power of the Panchayati Raj system that is provided by the state legislatures is required to authorise the Panchayats to become institutions of self-government at the primary level. The responsibilities such as to prepare plans for social justice and economic development. The schemes social justice and economic development as mentioned in XI schedule, there are 29 important matters mentioned in the XI schedule are rural housing, health, and sanitation, drinking water, agriculture, the welfare of weaker sections, agriculture, social forestry, etc.
There are three-tier structures of the Panchayat Raj system function.
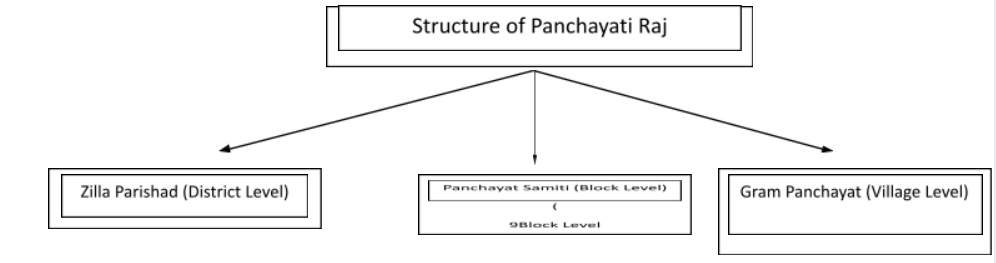
The Panchayati Raj system plays a vital role in the village local government to develop the village in special areas, such as health, women development, primary education of children, child development, women participation in local government, agricultural development, etc. There are several states which do not have Panchayat Raj system functions, some of these states are Mizoram, Nagaland, and Meghalaya.
Conclusion
It is to conclude that Panchayat Raj system functions are the functions that all Panchayati Raj institutions perform; the functions which they perform are related to Panchayati Raj as specified in state laws. The Power of the Panchayati Raj system that is provided by the state legislatures is required to authorise the Panchayats to become institutions of self-government at the primary level.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





