The term “Mole” was first introduced by Wilhelm ostwald. Mole concept connects the macroscopic to the molecular or atomic level. As it connects these levels, it allows chemists to weigh and count atoms or molecules. With the help of moles, it becomes easy to measure large objects like elephants by counting and small objects like nails, rice by weight.
Mole Concept
A substance is defined as “anything that has mass and occupies space.
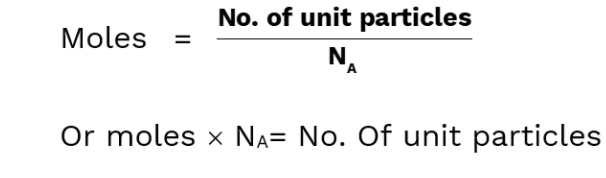
One mole of pure substance contains as many unit particles as there are number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of pure C12 sample.
1 mole substance =6.0214076 x 1023 unit particle of that element
6.0214076 x 1023= NA (Avogadro’s Number)
For a substance ,
Example
- A mole of water (H2O) has 6.02214076 x 1023 molecules with a total mass of 18.015 grams and an average mass of 18.015 daltons, giving it an atomic mass number of 18.015. Each material has the same number of atoms or other particles in a mole. The molecular weight of an element is linked to its mass in the following way: A mole of carbon-12 atoms is composed of 6.02214076 1023 atoms and weighs 12 grams.
- One mole of oxygen has the same amount of atoms as carbon-12 by definition, but it weighs 15.999 kilos. As a result, oxygen has a larger mass than carbon.
Certain materials may need more precise descriptions of their constituent particles than can be provided by a range of chemical standards. The mole mass of a substance is the same as its atomic or molecular mass, expressed, for example, in grams.
Molar mass
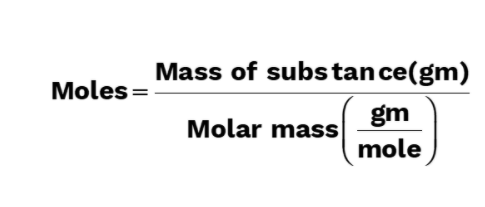
Molar mass is mass of one mole substance and is expressed in gram/mol,
Molar mass is molecular weight in grams. The molecular weight is sum of atomic weight of constituent atoms in a molecule .When discussing the same concept, ‘molecular mass’ , ‘molar mass’ and ‘molecular weight’ are often used interchangeably in the area of science where distinguishing between them is unhelpful.
Molar mass = Mass of NA unit particles of substance
= Atomic mass or molecular mass in grams
For a substance,
Molar mass of substance = mass of substance(g)/Moles
Examples
1. consider an example of helium having mass 4 gram.
Number of moles = 4 g / 4g mole-1 = 1
2. In most cases, the molar mass of a molecule is simply the average mass in daltons. The molar mass of water, for example, is 18.015 g/mol.
Knowing molar mass for a substance is great for calculations of chemical reactions. However, for most practical purposes, it cannot be utilised as individual particles cannot be weighed and don’t matter in most practical uses. Macroscopic terminology must be used while calculating mass.
Molecular weight is the mass in grams of one mole of a given chemical. Consequently, the unit of measurement grams per mole is specified in the molar mass definition.
The atomic, molecular, and molar masses are all connected in the case of carbon-12. It’s a two-part process. It is important to remember that one carbon-12 unit equals precisely one-twelfth of an asteroid’s mass (atomic mass). To put it another way, carbon-12’s molecular mass is exactly 12 grams per mole.
The atomic and molecular weights of carbon-12 are identical. Nuclear mass is measured using atomic mass units, while molar mass is measured using grams per mole units.
The molecular and molar masses of the various compounds are directly related to their formula groups and molar masses.
It is the mole ratio of the final solution that determines the molar concentration of a solution. In most cases, the mole per litre (mol/L) is used in place of the standard SI unit, the mole per cubic metre (mol/m3).
A substance’s molar fraction, also known as its mole fraction, may be calculated by dividing its molecular weight in a solution by the total of the molecular weights of all its other constituents.
Conclusion
Mole concept is an inherent part of a substance’s atomic properties and general chemistry. Atoms and molecules are the smallest of all objects in terms of both size and mass. When discussing weight, molar mass may be used to indicate the weight of one sample mole. The molar mass of a material is expressed in grams, with one gram equating one mole. The “molar mass” is the average mass of a molecule, given in daltons.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






