Introduction
Whenever we need to measure mass, length, speed, or distance, we always need some units like kilogram, meter, and kilometer. So, in this chapter, we will discuss the branches of various physical quantities. Units and measurement is one of the fundamental and most important physics topics. In this topic, we will study the various units and measurements and why we need them.
Units and Measurement
To calculate the physical quantities like time, mass, and unit of length, we need some standard of measurement. This standard of measurement is called the unit of a physical quantity. The unit means the standard criteria accepted by all parts of the society in some sense.
Fundamental Physical Quantity/Units
It is the physical quantity, which does not need any other physical amount to express it. The units of fundamental physical quantities are known as basic units.
For example:
In the MKS system: mass is expressed as kilogram, unit of length is expressed as meter, time is described as second
In the CGS system: length is expressed in centimeter, mass is said in gram, and time is defined in a second
Why do we need standard units and measurements?
Imagine a condition when a boy wants to purchase a blue-colored t-shirt, so he goes to a shop. The shopkeeper knows and speaks only English. The boy asks, “pólót akarok”. The shopkeeper was surprised and said, “What?!” The boy asked for a blue-colored t-shirt, but he said it in Hungarian. The shop owner could not understand anything as Hungarian is not a standard language.
Similarly, many systems and units are in place for calculating various quantities like area, mass, length, volume, etc. For example, an acre is a traditional way of measuring size in India. One acre is equivalent to 4046 square meters according to the metric system.
So, now you can assume how difficult it will be to measure the quantities of no standard terms introduced.
Similarly, the temperature is calculated in degrees celsius, but the length of a rod cannot be measured in the same unit. Every quantity has its way of measurement.
Physical Quantities
The quantities that can describe the law of physics are physical quantities. All of the physical quantities are measurable. The physical standard amounts are time, length, mass, temperature, resistance, pressure, and resistance.
Classification of physical quantities
The physical quantities are classified into
(i) Fundamental quantities or base quantities.
(ii) Derived quantities.
Fundamental Quantities are those physical quantities that are independent of each other.
Derived Quantities are those which can be expressed in terms of Fundamental.
Units
A similar standard used to determine physical quantities is known as a unit. There are basically two types of units that exist:-
(i) Fundamental Units
The units which are for the fundamental quantities are known fundamental units.
(ii) Derived Units
The units of other physical quantities derived from the fundamental units are known as derived units.
System of Units
- In FPS System: length is defined in the foot, mass is determined in the pound, and time is expressed in seconds
- In the CGS System: length is defined in centimeters, mass is expressed in grams, and time is limited in the second
- MKS System: length is defined in meter, mass is expressed in kilogram, and time is defined in the second
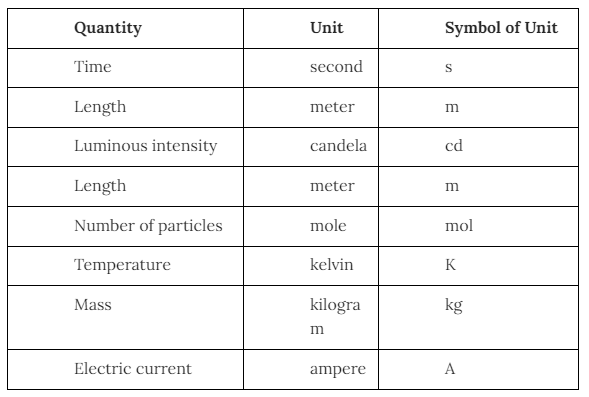
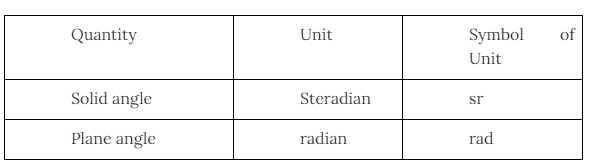
There are eight basic units and two, derived units we will study in this chapter. So, go through the table given below for a better understanding:-
Basic Units
Derived Units
What do you understand about the Dimensional Formula?
Dimensional formula of any physical quantity is a term that defines how and which of the base quantities are added in a particular.
Syntax of dimensional formula
(1) Physical Quantity should be written on left hand side of the equation.
(2) All the fundamental quantities like mass, length, and time should be written on right side of the equation.
(3) substitute M, L, and T in place of mass, length and time.
(4) write the given powers of terms.
Properties of Dimensions
(1) Dimensions did not rely on a system of the units.
(2) similar quantities can be subtracted or added .
Examples of some derived Quantities
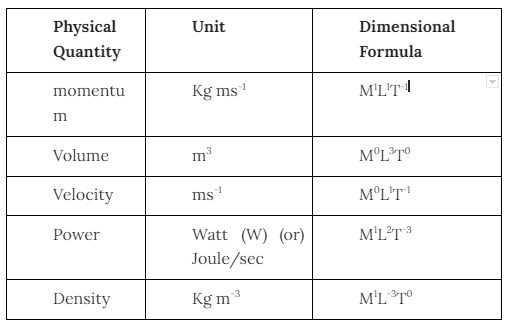
Conclusion
In this chapter, you have read about Unit and Measurements containing various types of formulas that even includes dimensional formulas, the system of units, CGS, MKS, etc system, Basic units, and derived units. So, go through the complete notes of the units and measurements to secure maximum marks in the examination.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






