The total vector of all the forces on that charge due to the presence of another charges, taken once at a time, is the force on that charge due to a number of other charges. Due to the presence of other charges, the separate forces remain unaffected. This is considered as a superposition principle.
According to this superposition principle, the total force acting on a given charge is equal to the vector sum of forces exerted on it by all the other charges.
Principle of Superposition
The interaction between two points charges is explained by Coulomb’s law. If there are more than two charges, the force exerted on one charge as a result of all the others must be determined. Coulomb’s law does not provide the answer on its own. The combination of several charges is described by the superposition principle.
The overall force acting on a given charge is equal to the vector sum of forces exerted on it by all other charges, according to this superposition principle.
Suppose we have a system having n charges namely q1, q2…. qn. The force acting on charge q1 due to charge q2 is given as:
F12→= k* q1q2/r²21* r∧21
Here r21 is the unit vector from charge q2 to q1 and r21 is the distance between the charges q1 and q2. The presence of other charges in the surrounding area has no effect on the electrostatic force between two charges.
The force q1 acting on charge q3 is given as:
F13→= k *q1q3/r²31* r∧31
By doing this, the total force acting on the charge q1 due to all other charges is given by this formula
F1Tot= F12 + F13 + F14 +………………… F1n
F1Tot=kq1q2r2 21 r21 + q1q3r2 31 r31 + q1q4r2 41 r41 +… q1q2r2 n1 rn1
Explanation of principle of superposition
It has been proved experimentally that the vector sum of all the forces on a charge due to a number of other charges, taken one at a time, is the vector sum of all the forces on that charge due to the other charges. Due to the presence of other charges, the separate forces remain unaffected. This is known as the superposition principle.
Consider a system of three charges q1, q2 and q3.
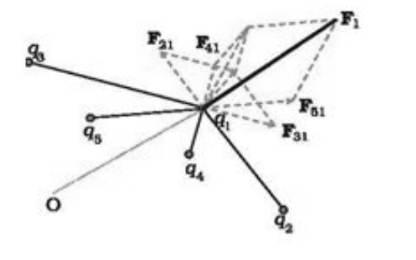
By performing a vector addition of the forces related to each of these charges, the force on one charge, say q1, due to two additional charges, q2, q3, may be obtained. Even if other charges are present, if the force on q1 due to q2 is represented by F12, F12 is given by following Eqn.
F12 =1/4π0 *q1q2/r²12 *r12→
Similarly, the force exerted on q1 by q3, denoted by F13, is given
F13 =1/4π0 *q1q3/r²13* r13→
Even when another charge, q2, is present, the Coulomb force on q1 is due to q3. As a result, the total force F1 generated on q1 as a result of the two charges q2 and q3 is given as
F1 = F12 + F13 =1/4π0 *q1q2/r² 12* r12→+ 1/4π0* q1q3/r² 13* r13→
The above force computation can be extended to a system with more than three charges, as shown in Fig (b). then
F1 = F12 + F13+…+F1n =1/4π0[q1q2/r² 12* r12→+q1q3/r² 13* r13→+……q1qn/r² 1n* r1n] = =q1/4π0i=2nq1/r² 1i *r1i→
The vector sum is determined by using the parallelogram law of vector addition. Coulomb’s law and the superposition principle are the foundations of electrostatics.
Uses of principle of superposition
The superposition principle has various uses in physics, but in basic, it is a method of combining the electric fields of several charges to create a more complex electric field. It’s a fantastic theorem because it simplifies rather than complicates things.
When it rains on a lake, the ripples all flow through each other, resulting in a pond with many separate, circular waves. In the same way, all of the voices in a room can be heard at the same time. You can normally only pay attention to one person at a time. The sound waves do not collide with one another. The notion of superposition also applies to phenomena we can’t observe, such as electric fields.
When comparing simple land-use changes to simultaneous land-use changes, the idea of superposition is used to discover locations where the atmospheric reaction is either enhanced or lessened. The findings illustrate that nonlinear behaviour of a given amount can occur in locations where the quantity is not greatly changed, and that a quantity can be changed significantly without detecting nonlinearity
Conclusion
The total vector of all the forces on that charge due to the presence of another charges, taken once at a time, is the force on that charge due to a number of other charges. Due to the presence of other charges, the separate forces remain unaffected. This is considered as the superposition principle.
The overall force acting on a given charge is equal to the vector sum of forces exerted on it by all other charges, according to the superposition principle. The interaction between two points charges is explained by Coulomb’s law. If there are more than two charges, the force exerted on one charge as a result of all the others must be determined. Coulomb’s law does not provide the answer on its own.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






