In the field of electromagnetism, magnetic flux is an important physical quantity. It is the overall magnetic field that flows across a certain area that is measured. Magnetic flux is measured in several ways depending on the location chosen.
The magnetic flux will be discussed in depth in this article, as well as other quantities such as magnetic field lines and magnetic field. One of the four Maxwell equations, which is analogous to Gauss’s law, which we studied in electrostatics, will also be discussed.
Magnetic Field
We’ve all seen magnets attract iron nails held close to them, but how do they do it without really touching them? Fields may be used to explain this behaviour, thus we have a magnetic field in addition to electric and gravitational fields.
Magnets are materials that have an inherent magnetic characteristic and produce a magnetic field.
When a charge is static, it just produces an electric field; however, when the charge moves, it produces both an electric and a magnetic field. A magnetic field is created when a moving charge travels.
When an electric current flows through a conductor, the conductor’s free electrons are in motion. A

Magnetic Flux
The number of magnetic field lines passing through an area is known as magnetic flux. It denotes the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field travelling through the surface. The Greek letter Phi(ϕ) is used to represent it. Weber is its SI unit (Wb).
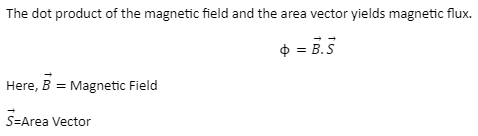
Magnetic Field Lines
Magnetic field lines, also known as magnetic lines of force, are a visual representation of the magnetic field. The magnitude and direction of the magnetic field are represented by the density and direction of lines in space.
The following are the properties of a magnetic field
- Two magnetic field lines will never cross.
- This is due to the fact that magnetic field lines determine the direction of the net magnetic field, and if they meet, the net magnetic field will have two directions, which is impossible.
- Lines of magnetic field create a closed loop.
- Magnetic field lines originate at the North Pole and end at the South Pole.
Gauss’s Law for Magnetism
One of Maxwell’s four equations for electromagnetic waves is Gauss’s law for magnetics.
The magnetic flux through any closed surface will be zero according to this law.

Corollary of Gauss Theorem
The sources and sinks of electric fields enclosed by the surface are the only sources and sinks of electric flux from any closed surface. Any charges outside the surface have no effect on the electric flow. Furthermore, electric field sources and sinks can only be electric charges. Changing magnetic fields, for example, cannot operate either as sources or sinks of electric fields.
The net flow for the surface on the left is non-zero because it encloses a net charge. The net flow is 0 because the right-hand surface is empty of charge. The Gauss law is simply a re-enactment of Coulomb’s law. The Gauss theorem can easily be applied to a point charge surrounded by a sphere to yield Coulomb’s law.
Application of Gauss’s Law
There are several application of Gauss Law which are listed below:

Conclusion
In this article we have studied Magnetic field and magnetic flux. We also have discussed Gauss’s Law of Magnetism. Magnets are materials that have an inherent magnetic characteristic and produce a magnetic field.
When a charge is static, it just produces an electric field; however, when the charge moves, it produces both an electric and a magnetic field. A magnetic field is created when a moving charge travels. The number of magnetic field lines passing through an area is known as magnetic flux. It denotes the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field travelling through the surface.
One of Maxwell’s four equations for electromagnetic waves is Gauss’s law for magnetics.
The magnetic flux through any closed surface will be zero according to this law.

 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out







