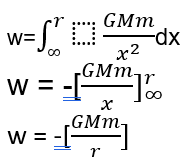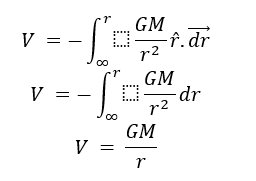Potential energy is an essential concept in physics that discusses the energy possessed by an object related to gravity or when it is elevated above ground level. Potential energy was the term Scottish scientist William Rankine adopted to represent the latent, or energy hidden within objects. So the article will define the basic concept of gravitational potential energy and the factors related to it. We will also focus on kinetic and potential energy and basic formulas and derivations.
Definition
Gravitational potential energy is the energy acquired by an object due to its vertical position or height. The energy is retained because of the gravitational attraction when we elevate objects against Earth’s gravity.
The gravitational potential energy of the large ball depends on two factors – the mass of the ball and the height to which it is raised. The gravitational potential energy is directly related to the mass of an object. The objects having greater mass possess higher potential energy. The gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to the height of an object. The higher an object is raised, the more gravitational potential energy is. The following equation can demonstrate these relationships:
Gravitational Potential Energy Formula
The equation for gravitational potential energy is:
⇒ GPE = m⋅g⋅h
Here, m represents the object’s mass, h represents the height, and g represents the gravitational strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth).
Derivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Equation
Where G is gravitational constant
M is the mass of the earth
m is the mass of the object
r is the distance between the object and the earth.
Since the work done is stored as its potential energy U. Therefore, gravitational potential energy at a point which is at a distance ‘r’ from the source mass is given by:
U = -GMm/r
Energy is a conserved unit. A system’s total energy remains the same, which means that an increase in kinetic energy cannot occur until there is a simultaneous decrease in potential energy. Energy converts from gravitational potential to kinetic energy when an object is dropped. But when the object is raised, the kinetic energy converts to gravitational potential energy.
Example of Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its vertical position or height. For example, a pendulum bob swinging above the tabletop contains potential energy that can be determined based on its height above the tabletop. By measuring the bob’s mass and the bob’s height above the tabletop, we can evaluate the potential energy of the bob.
Since the object is raised, there is a decrease in kinetic energy. To keep energy constant, the gravitational potential energy must increase.
Determining Gravitational Potential Energy
An object with a mass of 15 kg is at a point 10 m above the ground. What is the gravitational potential energy of the object?
Answer
We can define the object’s gravitational potential energy as the energy transferred to change its position from being on the ground to being 10 meters above the ground. This energy can be found using the formula
GPE=𝑚𝑔ℎ,
where ‘m’ is the object’s mass, ‘h’ can be the object’s height above the ground, and ‘g’ is the gravitational field strength in the region that the object moved through, in this case, from the ground to 10 meters above the ground.
We use 9.8 N/kg or 9.8 m/s2 for 𝑔. We have then that
GPE = 15×9.8×10 = 1470 joule.
Gravitational Potential
Gravitational potential (V) is the gravitational potential energy (U) per unit mass: where m is the mass of the object
V = U/m
where U is the gravitational potential energy of the test mass.
So, if the reference point is taken at an infinite distance, the potential is equal to the amount of work done per unit mass in bringing a test mass from an infinite distance to that point.
With the above definition, the gravitational potential due to a point mass M at a distance r from it is
Characteristics of Gravitational Potential
- While gravitational force is zero at infinity, it decreases as the object approaches the attracting body
- The gravitational potential is negative since the object moves from higher to lower potential
- It is maximum at infinity (zero)
- It is a scalar quantity
Conclusion
To conclude, potential energy is the energy present in an object due to its position relative to some zero position. An object contains gravitational potential energy if placed at a height above (or below) the zero height. So, for a better understanding, one must also study the topics related to kinetic energy and its conversion to potential energy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out