The impact of the earth’s massive magnetic field is responsible for a bar magnet’s north-south orientation. The earth’s magnetic field is thought to be created by electric currents travelling from the core to space.
Earth’s Magnetism
The Earth’s magnetic field, which resembles a bar magnet, spans millions of kilometres into space. The earth’s magnetic pole is located halfway between the Northern Pole and the Antarctic magnets at the North Pole. That is why the north pole of a compass magnet points north (north and south poles attract).
The Earth’s magnetic field stretches far and broad, although it has a very low field strength. It has a field strength of only 40,000 nanoteslas (nT), compared to 107 nanoteslas (nT) for a refrigerator magnet.
The magnetic poles of the earth are not aligned with the actual geographic north pole and south pole. Instead, Canada have the magnetic south pole, whereas Antarctica have the magnetic north pole.
Dynamo Effect
What causes the Earth to have its own magnetic field is unknown. The magnetic field was first imagined as a massive bar magnet placed roughly along the earth’s axis of rotation and within its centre. That was obviously far too simple to explain away.
According to the Dynamo Effect, the Earth’s magnetic field emerged due to the presence of metallic fluids such as molten iron and nickel in the planet’s outer core. The magnetic field is created by the convective motion of these fluids, which produces an electric current.
Ionization of outer layer
The Earth, as we all know, rotates both on its own axis and around the Sun. As the Earth’s outer layer gets ionised, this spinning generates an electric current. Because these ions are moving, they produce magnetic. However, because this magnetic field is so faint, the Dynamo effect is a more reasonable theory.
Cause of Earth’s Magnetism
The Earth’s magnetism is produced by molten iron and nickel convection currents in the core of the earth. Magnetic fields are created by charged particles in these currents. Solar winds are ionising charged particles that the sun discharges toward the planet. These particles are deflected by the earth’s magnetic field, preventing them from entering the atmosphere.
Solar winds would have damaged our atmosphere, making life on Earth uninhabitable if this magnetic shield had not been present. Mars is an example of this, where the lack of a magnetic field has resulted in an atmosphere unfit for life.
The earth’s magnetic poles and geographical north and south poles are not in line with one another. The southern magnetic pole is located in Canada, whereas the northern magnetic pole is located in Antarctica. Earth’s magnetic poles are angled away from the rotational axis by about 10 degrees.
Components of the Earth’s Magnetic Field
There are three components of earth’s magnetic field which are used to determine the magnitude and direction of the earth’s magnetic fields. These three components are given as:
Magnetic Inclination
Magnetic Declination
Horizontal Component of earth’s magnetic field
Magnetic Inclination
The angle of dip is another name for the magnetic inclination. It’s the angle formed by the horizontal plane on the surface of the earth. The magnetic equator has a 0° angle of dip, while the magnetic poles have a 90° angle of dip.
Magnetic Declination
The angle between true north and magnetic north is known as magnetic declination. On the horizontal plane, true north is never in the same place and varies based on the location on the earth’s surface and the passage of time.
Horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
Horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is again divided into two sub parts, the horizontal and vertical component of earth’s magnetic field.
Formula for the Earth’s Magnetic Field
The formula for earth’s magnetic field is given as
tan A = BV/BH
sin A = BV/B
cos A = BH/B
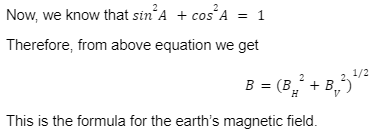
Conclusion
The impact of the earth’s massive magnetic field is responsible for a bar magnet’s north-south orientation.
The Earth’s magnetic field, which resembles a bar magnet, spans millions of kilometres into space.
According to the Dynamo Effect, the Earth’s magnetic field emerged due to the presence of metallic fluids such as molten iron and nickel in the planet’s outer core.
The Earth’s magnetism is produced by molten iron and nickel convection currents in the core of the earth.
There three components earth’s magnetic field which are given as:
- Magnetic Declination
- Magnetic Inclination (or angle of dip)
- Horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field.
The formula for the earth’s magnetic field.

 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






