An electrical cell is a “power supply” that turns chemical energy into electrical potential energy by allowing positive charges to flow from one terminal to the other via an external circuit. This is known as Current.
A cathode and anode electrode are used in an electrochemical cell. Electrodes are materials that participate in chemical reactions with the electrolyte. Let us study more about the electrical cell and how it is made up of examples in this article.
Electric Cell
Volta proposed in 1800 that certain fluids can provide continuous electric power when utilized as a conductor. The voltaic cell was developed at the beginning of this discovery. Following this, other scientists became involved in the advancement of electric cell technology.
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy is known as an electric cell. It is made up of two electrodes that are submerged in an electrolyte. A battery is made up of several electric cells that are connected together. When a battery or cell is connected through the circuit, electrons travel from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Chemical reactions in a battery create potential differences between its terminals. The energy required to move the electrons through the circuit is supplied by the potential difference.
As a result, a cell or battery is a chemically powered, self-contained device that generates a limited quantity of electrical output when needed. A cell progressively turns the chemical energy it stores into electrical energy, which it then uses. The energy generated by a battery is not the same as the energy we receive from an electric power plant in our houses. Fuel-based energy requires cables to transport it from one location to another, whereas battery-based energy is portable, as evidenced in mobile phones, laptops, and electric cars.
Working of an Electric Cell
An anode (- electrode), a cathode (+ electrode), and an electrolyte are the three components of a cell. An electrical circuit connects the positive and negative sides, or cathode and anode, respectively. The electrolyte, which can be a liquid or a dry powder, is dipped into these two electrodes. Chemical processes occur within the electrolyte when this cell is connected to an external circuit.
Positive ions and electrons are created near the negative electrode as a result of these reactions. From the external circuit, electrons travel towards the positive electrode, while positive ions migrate into the electrolyte. At the positive electrode, the electrons recombine with the positive ions in the electrolyte. As a result, the circuit is complete, and our device is ready to use.
A chemical reaction known as the oxidation-reduction reaction is required for a cell to function. The electrolyte facilitates the reaction between the cathode and the anode. An electrode, known as the anode, becomes negatively charged as a result of the oxidation reaction. The opposite electrode, the cathode, becomes positively charged as a result of the reduction reaction.
There will be electron mobility between two reactive metals when they are immersed in the same electrolyte solution. The one metal will lose electrons, while the other will acquire them. The difference in the concentration of electrons around the two metal electrodes creates a potential gradient between them.
Any electrical device can use this potential difference as a voltage source. It’s important to remember that ions only flow through the electrolyte, which prevents electrons from flowing from the anode to the cathode. As a result, we can only get electric current from the battery’s terminals.
Cell Connected in Parallel
When a collection of cells is connected in parallel, all of the cells’ positive terminals are connected at one place, and all of the cells’ negative terminals are connected at another. The positive and negative terminals of a battery are formed by these two places.
Let n cells are connected in parallel, and a resistance R is connected in parallel to the cells between the places A and B, as illustrated in the diagram below. If the EMF is and the internal resistance of each cell is r, then
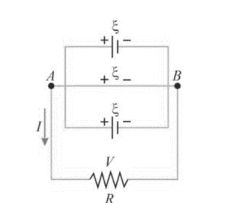
Then the Equivalent internal resistance of the battery is given by:
1/req=1/r+1/r+…n terms=n/r
req=r/n
Hence, the total resistance of the circuit is given by:
=req+R=r/n+R
Hence, the total current flowing through the circuit is:
I=total emftotal resistance=rn+R
If r ≫ R
I=nϵ/r
Here, the total current will be n times the current of a single cell.
If r ≪ R
I=nϵ/nR=€/R
As a result, the total current delivered by the battery equals the current due to a single cell in this case. Connecting cells in parallel is only useful when the external resistance of the cells is less than the internal resistance of the cells.
Application of an electric cell
The invention of the electric cell changed the direction of history. The energy system, which had previously only been limited to fuel and steam-based technologies, was overhauled. Since an electric cell is a portable and easily accessible kind of energy, it was possible to build gadgets that required less power to operate. We now have photovoltaic cells, solar cells, lithium cells, and batteries, all of which share the same basic design. Watches, satellites, electric car batteries, inverters, toys, TV remotes, and phones all use cells. In the medical field, these cells are commonly used to power hearing aids and pacemakers.
Conclusion
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy is known as an electric cell. An electric cell is made up of three major components. Within an electrolyte, it comprises two electrodes or electrical terminals. For convenience and safety, the entire equipment is normally placed inside a metal or plastic outer casing. A chemical reaction known as the oxidation-reduction reaction is required for a cell to function. The electrolyte facilitates the reaction between the cathode and the anode. Chemical processes occur within the electrolyte when this cell is connected to an external circuit.
Positive ions and electrons are created near the negative electrode as a result of these reactions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






