Incident angle can refer to the number of frames: in optics, incident angle is the angle generated by the radiation line with a line drawn perpendicular from the point of contact in the area. In aerodynamics, the incident angle refers to the angle between the aircraft wing and the longitudinal axis of the fuselage. Sometimes, the term ‘angle of incidence’ is used interchangeably with the term ‘angle of attack’, which refers to the angle between uninterrupted air flow and the sound of an airplane wing.
Definition of angle of incidence
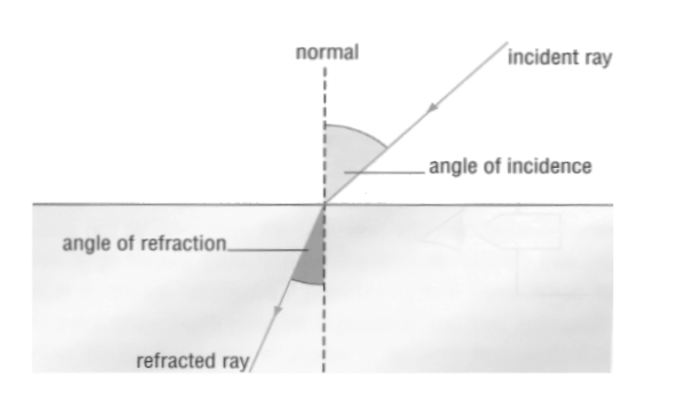
In Physics, the incident angle can be expressed as the angle formed between the radiation transmitted locally and the normal line to the point of occurrence at the same location. When a ray of light falls on a mirror, it appears in reverse. A ray of light strikes a spot somewhere. The straight line from that point, at 90 degrees upwards, is known as normal. Event angle is a standard built-in angle and light beam. We need to study in detail the concept of light exposure in order to understand the angle of inclination. This article will bring you information about the angle of inclination and other important concepts related to this topic.
1–>Here are some important facts about the angle of inclination:
2–>The ray of light is the beam that strikes first on the smooth surface of the mirror.
3–>The radiation shown is the radiation from the ray scene.
4–>The point of the scene is the place where the light rays are transmitted.
5–>Normal is known as a perpendicular line drawn in the same area.
We can see this by a diagram
What is the Key concept for the angle of Incidence?
When a ray of light is displayed on the surface, it rotates at an angle equal to the angle of incident.
–>A ray of light that begins to strike the surface in order to be seen continuously is known as an incident ray.
–>The lightning bolt strikes at an area known as an incident point at a certain angle called the incident angle.
–>A line drawn perpendicular to the scene is known as normal.
–>The beam of light reflected back after hitting the surface is known as the reflected beam.
Read about the formula for angle of incidence
The hypothetical law states that the angle of inclination is equal to the displayed angle. Therefore, the angle of inclination and reflection remains the same, and is in the same position as usual.
i = r
Where ‘i’ is the angle of incidence
- and ‘r’ is the angle of reflection
Incident angle = 90° – angle generated by the ray of light at the top.
Now we think about the what is the angle of reflection and why we use with the angle of incidence.so the relation between angle of incidence and angle of reflection is given below—————
Now, relation of angle of reflection and angle of incidence
- Snell’s law states that the sine of the refraction angle to the sine of the incident angle is constant and equals the speed of the phase of the two passing paths, defining the relationship between the incident angle. and the refraction angle.
- A ray of light strikes the flat surface of a mirror. From the scene, the same ray is dispelled. The point is separated perpendicular, which separates both angles. The incident angle and the refracted ray angle can be associated using normal.
- A ray of light is in contact with two different winds. The first is a very small medium well, and the second is thick. Compared to light speeds in a dense area, a rare medium has a faster speed. The medium has a significant influence on incident angle and refraction.
- Air and any other type of gas are an example of an unusual environment. Dense materials include glass, diamonds, and paraffin. Light speed is reduced within the denser medium, but• there is no resistance to light speed in any rare medium.
- Incident angle can be calculated using the Snell Act.
sin isir r = n2n1
Where –>
i = incident angle
r = refraction angle
n1 = event index
n2 = refracting medium index.
Examples of angle of incidence
–>When a wave of earthquakes collides with a stratum, it forms a sharp angle. The angle of inclination is 0, the wavefront is parallel, and the ray path is perpendicular, or normal, to the contact in the normal position.
–>The angle created between the local radius and the common line until it occurs in the same area is known as the incident angle. When a ray of light hits the top of a mirror, it returns to the source.
–>The angle formed by the rays of sunlight that collide with the vertical line; for example, an area facing the sun has a 0-degree angle, and a solar system (such as the sun’s rays hitting a horizontal roof) has an incident angle of 90°. Sunlight with a 90° incidence angle is absorbed, while low-angle light is visible.
Conclusion
The angle generated by the beam of light usually drawn at the scene when it falls into the contact area is known as the incident angle. If the path of the light source collides with a line corresponding to a visible connector, it creates an incident angle. The normal produced angle and the ray of light are called the incident angle.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






