The rate at which one quantity changes in relation to another is referred to as differentiation. Speed is calculated using the rate of change of distance with respect to time. This speed at each instant differs from the calculated average. Slope, which is nothing more than the instantaneous rate of change of distance over time, is the same as speed.
Differentiation is defined as the ratio of a small change in one quantity to a small change in another that is dependent on the first quantity. Differentiation determines the maximum or minimum value of a function, the velocity and acceleration of moving objects, and the tangent of a curve. If y = f(x) and x is differentiable, the differentiation is denoted by f'(x) or dy/dx.
Differentiation
In mathematics, differentiation is the process of determining the derivative, or rate of change, of a function. In contrast to the abstract nature of the theory, the practical technique of differentiation can be carried out using purely algebraic manipulations, utilizing three basic derivatives, four rules of operation, and knowledge of how to manipulate functions.
Differentiation is a mathematical concept used to calculate rates of change. In mechanics, for example, the velocity is the rate of change of displacement (with respect to time).
Differentiation principle
The slope of the tangent to the curvey=fx at x,fx is the geometrical meaning of the derivative of y=fx
The first differentiation principle is to compute the function’s derivative using the limits. Let f=y be a curve function (x). Consider a point P on a curve with coordinates(x, f(x)). Consider another point Q on the curve with coordinates(x+h,f(x+h).
PQ is now the curve’s secant. The slope of a curve at a given point is equal to the slope of the tangent line at that same point. We know that the slope of the secant line is
(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
Rate of change
The rate of change function is defined as the rate at which one quantity changes in relation to another. Simply put, the rate of change divides the amount of change in one item by the corresponding amount of change in another.
Rate change Differentiation
The rate of change of a function, such as y=fx, is determined by observing the amount of change in y in relation to a change in x. It is commonly referred to as “rise over run” because it is the amount of vertical change (“rise”) divided by the amount of horizontal change. This calculates the slope of a line drawn between the starting and ending points (x1, y1)and (x2,y2)
However, if the function is not linear, the computed rate of change is only a rough approximation. Because the curve’s shape (and thus slope) may change significantly between the initial and a simple slope calculation is important information about the curve.
To gain a better understanding of the curve’s behavior, we differentiate the function we take the derivative. Finding the slope over a small region of the curve, so small as to be infinitesimal—-is required. Instead of finding the slope between two points, the effect is to find it at a single point.
The “difference quotient” is a formal way to express this:
f‘ (x) =fz+h-f(z)h
Rate change formula
The rate of change formula describes the relationship between how one quantity changes in relation to how another quantity changes. The rate of change from y coordinates to x coordinates can be calculated as yx = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
the rate of change m of a linear function is represented in the slope-intercept form for a line: y=mx+b whereas the rate of change of functions is otherwise defined as
fb-f(a)b-a
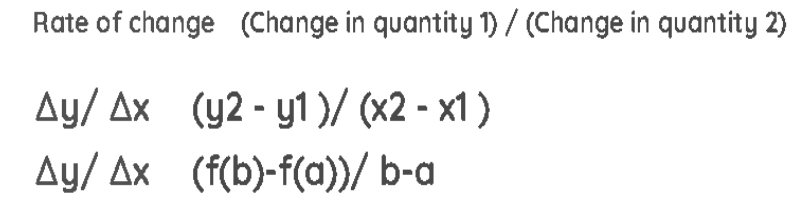
Rate of Change Formula Applications
The rate of change describes the rate at which something changes over time.
Travelled distance by car in a given amount of time.
For every volt of increased voltage, the current through an electrical circuit increases by some amperes.
It is also regarded as an important financial concept. It enables investors to identify security momentum as well as other trends.
Work completed per unit time
Work completed and the number of people required to complete it
Conclusion
The instantaneous rate of change is a measurement of the rate of change, or slope, of a curve at a specific point in time. As a result, the derivative gives the instantaneous rate of change.
We can calculate rates of change using differentiation. It, for example, enables us to calculate the rate of change of velocity with respect to time (which is acceleration). It also allows us to calculate the rate of change of x with respect to y, which is the gradient of the curve on a graph of y against x.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






