A parabola is a curve equation in which a point on the curve is parallel from both a fixed point and a fixed line. The fixed point is known as the parabola’s focus, and the fixed line is known as the parabola’s directrix. It’s also worth noting that the fixed point is not located on the fixed line. A parabola is a locus of any point that is equidistant from a given point (focus) and a given line (Directrix). The parabola is an important curve in coordinate geometry’s conic sections.
Parabola
The terms listed below will help you understand the characteristics and parts of a parabola.
Focus: The focus of the parabola is the point (a, 0).
Directrix : The directrix of the parabola is a line drawn parallel to the y-axis and passing through the point (-a, 0). The parabola’s axis is perpendicular to the directrix.
Focal chord: The focal chord of a parabola is the chord that passes through the parabola’s focus. The parabola is cut in two places by the focal chord.
Focal distance: The focal distance is the distance between a point (x1, x2) on the parabola and the focus. The perpendicular distance of this point from the directrix is also equal to the focal distance.
Eccentricity: (e = 1) Eccentricity It’s the proportion of a point’s distance from the focus to its distance from the directrix.
Form of Parabola
Parabola Formula
Parabola Formula helps in representing the general form of the parabolic path in the plane. The formulas for calculating the parameters of a parabola are as follows.
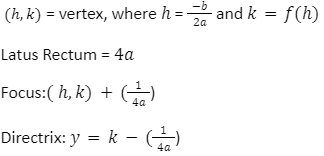
Parabola equation
A parabola’s general equation is y=a(x-h)2+k or x=a(y-k)2+h where (h,k) is the vertex.
A regular parabola’s standard equation is y2=4ax
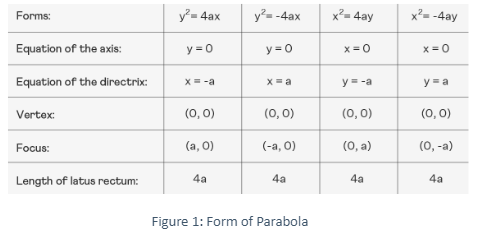
Parabola Equations in Standard Form
There are four standard parabola equations. The four standard forms are based on the parabola’s axis and orientation. Each of these parabolas has a different transverse axis and conjugate axis. The four standard parabola equations and forms are shown in the image below.
The following are the results of using the standard form of equations:
- In relation to its axis, a parabola is symmetric. The axis of symmetry is along the x-axis if the equation has a term with y2, and the axis of symmetry is along the y-axis if the equation has a term with x2
- The parabola opens to the right if the coefficient of x is positive and to the left if the coefficient of x is negative when the axis of symmetry is along the x-axis.
The parabola opens upwards if the coefficient of y is positive and downwards if the coefficient of y is negative when the axis of symmetry is along the y-axis.
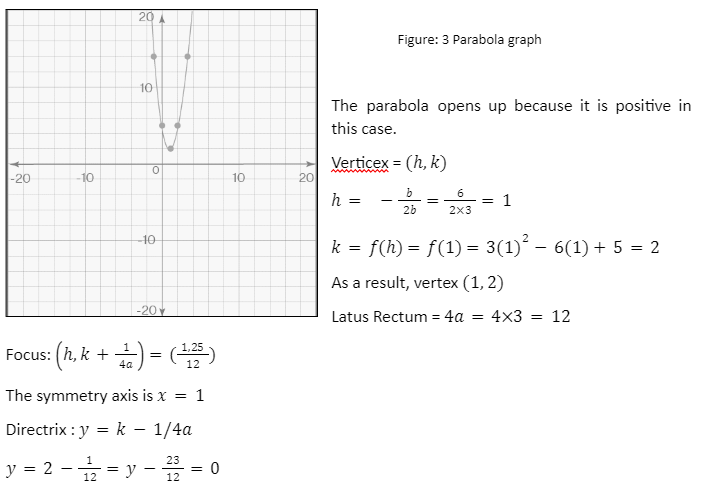
Parabola graph
Take the equation y=3×2 -6x+5 as an example. A = 3, b = -6, and c = 5 for this parabola. The graph of the given quadratic equation, which is a parabola, is shown below.
Conclusion
A parabola is a curve equation in which a point on the curve is parallel from both a fixed point and a fixed line. The fixed point is known as the parabola’s focus, and the fixed line is known as the parabola’s directrix. It’s also worth noting that the fixed point is not located on the fixed line. A parabola is a locus of any point that is equidistant from a given point (focus) and a given line (directrix). The parabola is an important curve in coordinate geometry’s conic sections. In physics and engineering, parabolas are frequently used in things like the design of automobile headlight reflectors and the paths of ballistic missiles.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






