The root of unity is a complex number that yields 1 when raised to the power of a positive integer n. These roots are used in various branches and topics of mathematics, such as number theory. It is also known as the de Moivre system. The cube root of unity is written as 3 1 and has three roots. The three roots of the cube root of unity are 1, ω, ω2, which when multiplied together yields the answer unity. One of the roots of the cube root of unity is a real root, while the other two are imaginary roots. The following are the values of the imaginary cube root of unity. Cube Unity’s Roots the root of unity is a complex number that yields 1 when raised to the power of a positive integer n. These roots are used in various branches and topics of mathematics, such as number theory.
Definition Cube Root of Unity
The cube root of unity is written as 3 1 and has three roots. The three roots of the cube root of unity are 1, ω, ω2, which when multiplied together yields the answer unity. One of the roots of the cube root of unity is a real root, while the other two are imaginary roots. The following are the values of the imaginary cube root of unity.
Furthermore, the imaginary cube roots of unity are represented by the symbol ω, ω2 which is known as omega. Omega and omega squares are the imaginary roots of the cube root of unity.
Cube Root identities
Cube root identities are:
The cube root of unity is represented by the number 3√1 and has three roots. The three roots of the cube root of unity are 1, ω, ω2 which when multiplied yields the answer unity.
Cube Roots of Unity’s product
![]() How Do You Find The Cube Root Of Unity?
How Do You Find The Cube Root Of Unity?
As an expression, the cube root of unity can be represented.
It also has three roots. This expression can be simplified further by using algebraic formulas to find the three cube roots of unity.

Cube Root of Unity Properties
The cube root of unity has the following important properties.
There are two imaginary roots (ω, ω2) and one real root in the cube root of unity (1).
The sum of the cube roots of unity is equal to zero. (1+ω + ω2 = 0)
One imaginary root (ω) of the cube root of unity squared equals another imaginary root (ω2) of the cube root of unity.
The product of the imaginary roots of unity’s cube roots equals one.
(ω.ω2 = ω3 = 1)
Cube Root of Unity problem
Using the values of the cube root of unity, calculate the value of ω67.
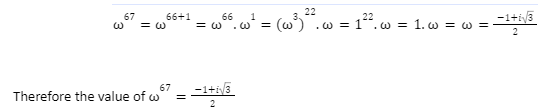
Conclusion
A cube root is a number that, when cubed, yields the radicand, whereas a square root yields the radicand when squared. Furthermore, the cube root of a negative number can be negative, whereas the square root of a negative number cannot. The cube root of unity has three roots: 1, ω, ω2, and 3. Here, the roots and ω2 are imaginary, and one root is a square of the other. The product of the imaginary roots of the cube root of unity is 1(ω.ω2 = ω3 = 1), and the sum of the cube roots of unity is zero. (1 +ω + ω2) = 0. Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, but they are particularly important in number theory, group character theory, and the discrete Fourier transform. When the field’s characteristic is zero, the roots are complex numbers that are also algebraic integers.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





 How Do You Find The Cube Root Of Unity?
How Do You Find The Cube Root Of Unity?
