An angle is a figure generated by two rays or lines that have a common endpoint in Plane Geometry. The name “angle” is derived from the Latin term “angulus,” which means “corner.” The two rays that make up an angle are called sides, and the shared endpoint is called the vertex. The angle in the plane does not have to be in Euclidean space.
Angles formed by the intersection of two planes in Euclidean or other space are called dihedral angles.
Positive Angle: If the angle is in opposite direction in which a clock moves , then it is called a positive angle.
Negative Angle: If the angle is in the direction in which a clock moves , then it is called a negative angle.
Angle Definition
Geometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with the measurement of shapes. It also emphasises the relative arrangement of the forms as well as their spatial characteristics. We all know there are two forms of geometry: 2D and 3D. Points, lines, rays, and flat surfaces are used to create all geometrical shapes before being divided. When two lines or rays converge at a single place, the measurement between them is called an “Angle.”
Best way to label the angles
The angles can be labelled in two distinct ways. They are as follows:
Method 1: Give the angle a name. Generally, the angle is denoted using lower case letters such as “a,” “x,” and so on, or with Greek letters such as alpha (α), beta (β), theta (θ), and so on.
Method 2: We may determine the angle by using the three letters on the shapes. The vertex should be the centre letter (actual angle).
for instance, ABCis a triangle. We can write ∠BAC = 60° to signify the angle A is equal to 60 degrees.
How to Measure the Angle?
Angles are usually expressed in degrees (°). A “protractor” is an important geometrical tool for measuring angles in degrees. A protractor is a device that has two sets of numbers that are pointing in opposite directions. The outer rim of one set goes from 0 to 180 degrees, while the inside rim of the second pair goes from 180 to 0 degrees.
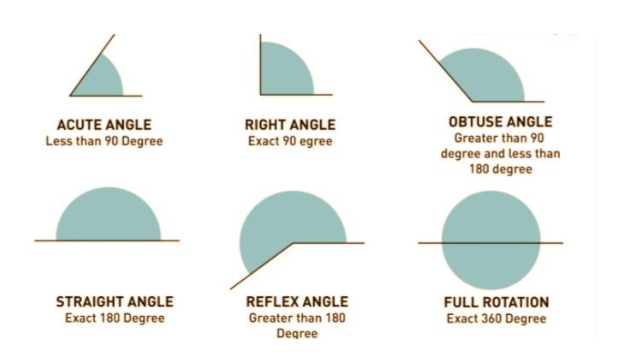
Types of Angles
Angles are categorised into the following categories:
- An acute angle is one that is smaller than 90 degrees.
- An angle that is exactly 90 degrees is called a right angle.
- An angle that is larger than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees is called an obtuse angle.
- An angle that is exactly 180 degrees is known as a straight angle.
- An angle that is more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees is known as a reflex angle.
- An angle that measures exactly 360 degrees is known as full angle.
It is further classified into numerous sorts based on these angles and lines, including complementary angles, supplementary angles, adjacent angles, vertical angles, alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, and so on.
When the transversal cuts two or more lines, it creates a series of angles. The pair of angles is given a name that is determined by the angle’s position in reference to the lines. There are two types of lines: parallel and not-parallel. The following are a few examples of important pairs of angles:
Corresponding Angles
- Alternate Interior Angles
- Alternate Exterior Angles
- Interior Angles on the Same Side of Transversal
- Supplementary Angles
- Adjacent Angles
- Vertical Angles
Let’s look at some of the most important theorems about lines and angles:
- When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, the alternate interior angles have the same measure.
- When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, the alternate exterior angles have the same measure.
- When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, the associated angles have the same measure.
- When a transversal cuts two parallel lines, the interior angles on the same side of the transverse are supplementary.
- When a straight line joins two lines, the vertical angles are congruent. There are two types of lines: parallel and non-parallel.
Angles’ Characteristics
Angles have the following key properties:
- The sum of all the angles on one side of a straight line is always equal to 180 degrees,
- The sum of all the angles around the point is always equal to 360 degrees.
Conclusion
The 6 types of angles are right angles, acute angles, obtuse angles, straight angles, reflex angles, and full angles. i.e
- An acute angle is one that is smaller than 90 degrees.
- An angle that is exactly 90 degrees is called a right angle.
- An angle that is larger than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees is called an obtuse angle.
- An angle that is exactly 180 degrees is known as a straight angle.
- An angle that is more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees is known as a reflex angle.
- An angle that measures exactly 360 degrees is known as full angle.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



