In probability, any subset of a sample space S, such as E, is referred to as an event. In probability, there are various sorts of events. We may also use the algebra of events to execute various operations on these.
Probability Algebra of Events
In probability, the algebra of occurrences consists of the following:
- Complementary Activity
- The ‘A or B’ Event
- The ‘A and B’ Event
- The ‘A but not B’ Event
Assume that A, B, and C are events connected with an experiment whose sample space is S, and that A, B, and C are subsets of S. Let’s go over each of these events’ algebra one by one.
Complementary Event
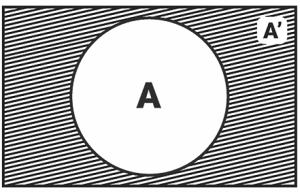
Every event A has a companion event A′, which is referred to as the complimentary event to A. It’s also known as the ‘not A’ event.
A′ = {ω : ω ∈ S and ω ∉A} = S – A
The event A is represented by A, the outcome associated with A is represented by, and the sample space is represented by S.
Using a venn diagram, we can depict the complimentary event as follows:
Take, for example, the ‘tossing three coins’ experiment.
The sample space connected with it can be written as follows:
S = Sample space = { HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, HTT, THT, TTH, TTT }
Let A represent the occurrence of obtaining ‘at least two heads.’
As a result, the outcomes associated with the event A = { HHT, HTH, THH, HHH are HHT, HTH, THH, HHH }.
As a result, we can conclude that event A did not occur for the outcome HTT. To put it another way, the event ‘not A’ has occurred.
As a result, A′ is the complementary event ‘not A’ of the event A.
A′ = { THH, HTT, THT, TTH, TTT }
The ‘A or B’ Event
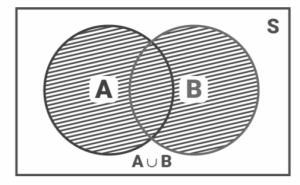
The Event ‘A or B’ is the union of two sets A and B, denoted by A ∪ B containing all those elements in A or B or both.
When there are two events linked with a sample space (sets A and B), then A ∪ B is either A or B or both. This event ‘A ∪ B’ is also called ‘A or B’.
Event ‘A or B’ = A ∪ B = {ω: ω ∈ A or ω ∈ B}
The following is the venn diagram representation of A or B :
Consider the experiment of simultaneously throwing two dice.
The sample space connected with it can be written as follows:
S = Sample space = { (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6) }
Let A be the event in which the total of two scores is a multiple of three, and B be the occurrence in which both dice have the same score.
The following are the outcomes of these events:
A = {(1, 2), (2, 1), (1, 5), (5, 1), (2, 4), (4, 2), (3, 3), (3, 6), (6, 3), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 6)}
B = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5), (6, 6)}
As a result, A ⋃ B = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 5), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 4), (3, 3), (3, 6), (4, 2), (4, 4), (4, 5), (5, 1), (5, 4), (5, 5), (6, 3), (6, 6)}
The ‘A and B’ Event
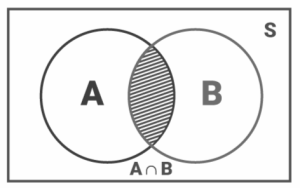
The ‘A and B’ event is the intersection of two sets of data. A B is the set of elements that are common both for A and B, i.e., elements that belong to both ‘A and B’.
If A and B are two events, then the set A ∩ B denotes the event ‘A and B’. It is represented as:
A ∩ B = {ω: ω ∈ A and ω ∈ B}
Using a Venn diagram, the set A ∩ B is shown below:
Consider throwing two dice at the same time once more.
The sample space connected with it can be written as follows:
S = Sample space = { (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6) }
Let A be the event of earning a score of 5 on the second die, and B be the event of getting a total of 10 & more than 10 on the dice.
The following are the outcomes of these events:
A = { (1, 5), (2, 5), (3, 5), (4, 5), (5, 5), (6, 5) }
B = { (3, 6), (6, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 5), (6, 6) }
As a result, A ∩ B = (5, 5), (6, 5)
The Event ‘A but not B’
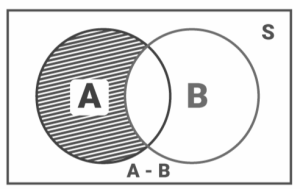
The set A – B, or difference of sets A and B, is the occurrence A but not B. It’s the collection of all the elements in A that aren’t in B. The set A – B can be calculated using the following formula:
A – B = A ∩ B′
Therefore, A – B = {ω: ω ∈ A and ω ∉ B}
The diagram below aids comprehension of occurrence A but not B.
Consider the following scenario: you’re rolling a dice.
S = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 } is the sample space.
Let A represent the probability of getting a prime number and B represent the probability of getting an even number.
The following are the outcomes of these events:
A = {2, 3, 5}
B = {2, 4, 6}
As a result, A – B = { 2, 3, 5 } – { 2, 4, 6 } = { 3, 5 }
Alt.
B′ = {1, 3, 5}
A ∩ B′ = { 2, 3, 5} ∩ {1, 3, 5} = {3, 5}
Thus, A – B = {3, 5}
Conclusion
Events related to the experiments are the results or outcomes of a random experiment. As a result, “head” and “tail” are the outcomes of a random experiment involving tossing an unbiased coin, as well as events related to the experiment. Similarly, the outcomes of a random experiment in which an unbiased dice is thrown from a box are 1, 2, 3,…., 6, and each outcome is an event related to the experiment. Similarly, the result is an occurrence that occurs as a result of this experiment. The capital letters A, B, C, and so on are commonly used to signify events related to a random experiment.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






