The supply and demand theory gives a clear representation of the interaction between consumers and producers in a market. Both of these laws are closely interconnected to each other so that a change in one can affect the other drastically. Also, the product price plays a significant role in the shift in supply and demand of a product in an economy.
Today, in this article on the understanding of Effects of Shifts in demand and supply, you will get detailed information on supply and demand theory, Determinants of supply and demand, and other related topics. So, without further ado, let us get started with the introduction to Effects of Shifts in demand and supply in the economics study material.
What is Demand?
In simple terms, demand refers to the desire of the customer to buy particular goods and services without any worry of paying the price set for them during a given time frame. Choices and preferences are the foundations of demand that can be easily described in terms of benefits, profit, cost, and other crucial variables.
The amount of goods that the customer willingly buys is highly dependent on the cost of the commodity. There are mainly seven types of demand in the market. These include price demand, income demand, cross demand, direct demand, indirect demand, joint demand, and composite demand.
Determinants of Demand
Primarily, there are 5 major determinants of demand. These include –
- The prices of the goods and services
- Customer’s desire to buy a product
- The buyer’s income
- Prices of the related products include substitute products and complementary products.
- The future expectations of the buyer and seller.
When Demand Changes
There are several factors that lead to changes in demand for a product. These include –
- Value of the essential commodities
- Forecast of change in prices
- Value of substitute items
- Per capita income
- Population
- Preferences
The price of the product is highly determined by the increase or the decrease of the prices. Let’s have a look –
Demand increases
Every time the supply of the product remains constant; however, the demand rapidly rises, the demand curve tends to shift rightwards. If it continues to rise for a longer time, it surely impacts the equilibrium price. As a result, the rise in price leads to competition between producers.
Demand decreases
If the supply of the product remains constant, however, its demand falls with time at a steady speed, the demand curve tends to shift leftwards. In such cases, the condition of excess supply appears at the level of equilibrium. This condition increases the competition between all producers as to who is going to make the maximum sale.
What is Supply?
The concept of supply can be understood by the commodity quantity that a seller is willing to sell at a particular price. The supply in the market is highly determined by factors such as production cost, taxes imposed, and the firm’s expectations. The more the prices of the commodity will be, the seller will try to make maximum sales to earn a larger profit.
Determinants of Supply
There are mainly three determinants of supply. These include –
- Cost of the production – If the production cost increases, the supply of the product decreases.
- Taxes – In case of the taxes increase, the product supply will decrease. In such cases, the supply curve shifts to the left-hand side.
- The goal of the firm – Every firm has different goals except profit. Some of the common firm’s goals are social welfare and sales maximisation.
Changes In Supply
There are several reasons which could lead to the change in the supply of a product. These include –
- The expectation of future price change
- Technological advancement
- Cost of factors of production
- Number of manufacturers
- Cost of competitive products
- Aim of companies
- Taxes levied
When Supply Changes
In case there are alterations in the supply of the product, there are changes in the supply-demand curve. It can occur if –
Supply increases
If the demand remains the same, but the supply changes, the supply curves move towards the right-hand side. As a result, when the product supply increases, its demand at the level of equilibrium also rises. This condition gives rise to competition in the market-leading to a drop in product prices.
Supply decreases
The demand for the product remains the same, but the supply changes, the supply curve moves towards the left-hand side. As a result, when the supply of the product falls, it increases the demand to the level of equilibrium.
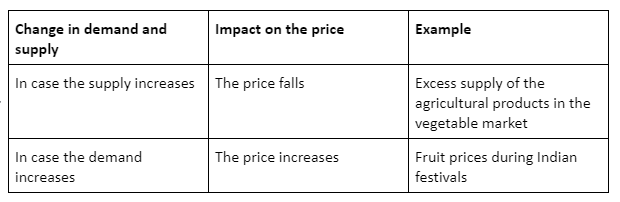
Change of Both Supply and Demand
Apart from the above-mentioned situations, there are several other market situations that make it even more complicated. Here are four major market situation that arises in real world scenario-
- Demand decreases, supply decreases
- Supply increases, demand decreases
- Demand increases, supply increases
- Supply decreases, demand increases
Conclusion
With this, we end our study material on the effects of shifts in supply and demand. In these supply and demand notes where we studied that demand refers to the desire of the customer to buy particular goods and services. The supply in the market is highly determined by factors such as production cost, taxes imposed, and the firm’s expectations.
We covered the effects of shifts in supply and demand, the determinants of Effects of Shifts in demand and supply, with supply and demand curve. Apart from this, we also mentioned changes in supply and demand and their effects in detail. We hope the effects of shifts in supply and demand study material must have helped attain a greater understanding of this topic.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






