Introduction
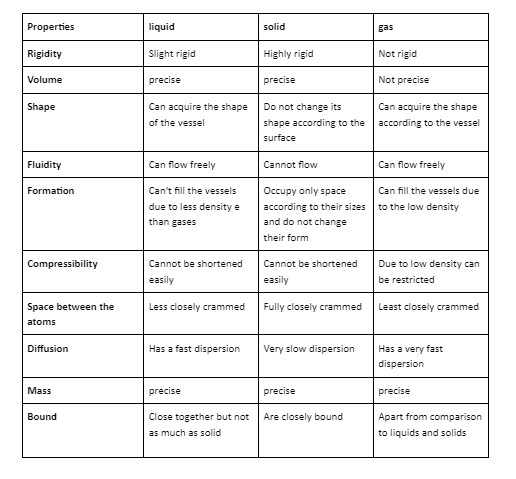
We are mostly encircled by solids and we utilise and manipulate them more frequently than liquids and gases in our daily life and activities. We can define solid in simple terms as a substance that has a fixed shape, size, and rigidity. There are various properties of solids that make them different from the liquids and gases like their binding force and the nature of particles of matter. Let us discuss it with an example, the particles of matter in gases and liquids are free to move inside their structure due to its fluidity property whereas particles of matter inside the solids can not move; they remain stationary due to its rigidity property. The solid-state of compounds largely depends on the properties of atoms such as the forces acting between them or their arrangement. For different applications of solids, we need them with widely different properties.
10 Properties of Solids
Solids are distinguished by their precise volume, shape, and high density. In a solid state, the constituent particles i.e. atoms, molecules, or ions of matter are organised in various structures. The investigation of solid-state is known as solid-state chemistry. In other words, we can name it materials chemistry which explores the structure, preparation, and properties of solid-state materials. There are 10 properties of solids which are as follows:
- Solids are incompressible which means the constituent particles are classified close to each other and due to this, there is inconsequential space between the constituent particles.
- Solids are rigid which is because of the lack of area between the constituent particles that makes them fixed.
- Solids have a precise mass due to which it has a portable arrangement of constituent particles.
- The intermolecular distance between molecules is short because of that the force between the constituent particles i.e. atoms, molecules, or ions is very strong.
- The constituents particles can only oscillate about their normal positions.
- The constituent particles of matter inside solid i.e. atoms, molecules, or ions are tightly packed together and bound by the strong attractive force
- Solids have fixed volume
- Solids are highly dense because their constituent particles are closely knitted together.
- Solids only take the space as much as their size and they maintain their shape.
- They don’t flow like liquids.
Types of solids
Solids are classified into two-state types that are based on the arrangement
- Crystalline Solids
- Amorphous Solids
Crystalline Solids
They are those that have a typical geometrical shape. For example, quartz, diamond, etc. the formation of constituent particles i.e atoms, molecules, or ions in the crystalline solids is ordered. They are also called true solids. They are anisotropic, which means their physical properties like a refractive index or electrical resistance show different values when they are scaled along with numerous directions in the same crystal. They have a pointed melting point and at a specific temperature, they start melting. crystalline solids have a precise shape and have a specific arrangement of particles. Crystalline solids show detachment property, that is when they are cut with the rim of a sharp tool they divide into two pieces and the just created surfaces are smooth and plain. crystalline solids have precise heat of fusion i.e. the amount of energy required to melt a given mass of solid at its melting point. Crystalline solids can be classified into four different types. They are as follows:
- Ionic solids
- Molecular solids
- Covalent solids
- Metallic solids
Amorphous Solids
They are composed of those solids that have the property of incompressibility and rigidity but to a specific magnitude. They do not have an obvious geometrical form or a long range of order. For Example, cotton candy, rubber, glass, plastic, etc. They can be moulded into different shapes and softened on heating. They have irregular shapes and do not form regular surfaces when they are cut with sharp tools. They are isotropic, which means the significance of any physical property would be exact along any direction due to the uneven arrangement of particles.
Conclusion
We can define solid in simple terms as a substance that has a fixed shape, size, and rigidity. There are various properties of solids that make them different from the liquids and gases like their binding force and the nature of particles of matter. Solids are substances that have fixed Legend size and shape. There are 10 properties of solids that make them differ from the 10 properties of liquids and gases.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






