Lewis shape may be simplified through representing -electron covalent bond through a sprint (−). Such a structural system specializes in the electrons concerned in bond formation. An unmarried sprint represents a unmarried bond, double sprint (═) is used for double bond and a triple sprint (≡) represents triple bond. Lone-pairs of electrons on hetero atoms (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, halogens etc.) might also additionally or might not be shown. Thus, ethane (C2H6), ethene (C2H4), ethyne (C2H2), and methanol (CH3OH) may be represented through the subsequent structural formulation. Such structural representations are referred to as whole structural formulations. These structural formulations may be in addition abbreviated through omitting a few or all dashes and indicating a variety of equal companies connected to an atom through a subscript. Resulting expression of the compound is referred to as a condensed structural system. Similarly CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 may be in addition condensed to CH3(CH2)6CH3. In the bond-line system, carbon and the traces representing carbon-carbon bonds are drawn in a zigzag style. Only atoms especially written are oxygen, chlorine nitrogen etc. terminals denote methyl (-CH3) companies (except indicated in any other case through a practical institution). Line junctions denote carbon atoms bonded to a suitable number of hydrogens required to fulfill valency of carbon.
Catenation
Unique asset of Carbon, of linking itself to different carbon atoms to present an open chain and/or cyclic system, is named as catenation. Catenation is determined in which atom to atom covalent bond is pretty strong. In carbon, C – C bond enthalpy may be very large (347.three kJ mol-1). So, carbon suggests catenation. Carbon atoms because of their tetravalency may be bonded to 3 or 4 carbon atoms through forming unmarried and a couple of bonds. Therefore, chains of carbon atoms can be linear, branched or cyclic
Isomerism
Compounds having equal molecular systems, however specific bodily & chemical homes are referred to as isomers and phenomenon is referred to as isomerism. Isomers may be recognized and outstanding from each other because of distinction in bodily and chemical homes. Broadly isomerism may be categorized into types:
- Structural isomerism
- Stereoisomerism
- Chain isomerism (additionally referred to as nuclear or skeletal isomerism)
Different skeletons of carbon chains are found in specific isomers. C5H12 has 3 isomers normal, iso and neo pentane. Isomers displaying chain isomerism belong to equal homologous collection Position isomerism Position of practical institution or a couple of bonds is specific in isomers. e.g. o, p and m isomers of equal compound. Butan-1-ol and butan-2-ol Metamerism Different alkyl companies are connected to equal practical companies in specific isomers. Ethers, esters, ketones, 2°-amines suggest Metamerism due to the fact they have got alkyl companies.
Tautomerism or demo tropism (dynamic equilibrium of tautomerism) or allotropes or kryptomerism
Tauto = equal, meros = element It is dynamic isomerism. Two isomers can in no way be separated. Isomers are referred to as tautomers or tautomerides It is due to presence of labile H in compound. Also referred to as desmotropism (desmos = bond, tropos = turn)
Keto-enol Tautomerism
Keto shape is greater solid because of more power of C−O π bond (87 kcal/mol) compared to C−C π bond (60 kcal/mol) In a few cases, enolic shape is stabilized through intramolecular hydrogen bonding (Chelation). When a benzene ring is found in enolic shape, double bond is in conjugation with the π cloud of benzene ring, then stabilization of enolic shape in addition will increase through conjugation. Polar protic solvents (e.g.- H2O, CH3OH) shape hydrogen bonding with keto shape and reduce enol content. Aprotic solvent increases enol content. (Solvation reasons alternate in entropy) If the Hydrogen atom oscillates among polyvalent atoms related collectively the gadget is referred to as dyad H – C ≡ N ↔ C N-H Hydrogen atom travels from first to 0.33 in atom the gadget is referred to as triad.
Ring-chain isomerism
Cyclic and open chain systems are viable through equal systems. e.g.- Cycloalkane and alkenes. Another instance is But-1-ene, Cyclobutane and methyl cyclopropane all are isomers
Stereo Isomerism
Geometrical isomerism (cis-trans isomerism) or configurational isomerism: It is prompted because of hindered rotation throughout C = C bond [or C= N or N= N bond (syn for cis & anti for trans is used) Conditions vital for compound to show off geometrical isomerism are; Compound ought to have as a minimum one C = C. Two companies connected to equal carbon atom ought to be specific. Difference in homes of cis and trans isomer Boiling factor: Higher for cis isomer. (excessive polarity of cis compound) Melting factor: Higher for trans isomer (because of symmetrical packing) Solubility, viscosity and refractive index of cis-isomer is greater than trans-isomer in a given solvent. Density: Higher for trans isomer (because of near packing) Dipole moment: Higher for cis isomer. Trans isomer has zero/much less dipole moment (or much less dipole moment.) Stability: In general, trans-isomer is greater solid and much less reactive than cis-isomer. Steric repulsion of the companies at the equal aspect in cis shape makes it much less solid and greater reactive than trans isomer. Cis-isomer bureaucracy cyclic compounds (because of nearness of companies) however trans isomer does now no longer shape). E and Z gadget of Nomenclature of
Geometrical Isomers
Cis and trans designations cannot be utilized in surprisingly substituted alkenes, therefore the want for E and Z gadget of nomenclature. In this gadget atoms/companies connected to every doubly bonded carbon are positioned so as of precedence, and a couple of on the idea of series regulations. Sequence regulations state that the institution or atom with better atomic mass has better precedence, double and triple bonds are dealt with as though they have got reproduction or triplicate unmarried bonds. This precedence gadget turned into advanced through Cahn, Ingold and Prelog and is referred to as CIP rule if companies of better precedence are on equal aspect of double bond, it’s miles assigned Z configuration and if on contrary aspect it’s miles assigned E configuration. E is derived from German phrase Entgegen = throughout or contrary Similarly Z is likewise derived from German phrase Zusammen = collectively
Geometrical isomerism in compound having C = N
- Syn – if H (or alkyl institution) are on equal aspect of C = N.
- Anti – if H (or alkyl institution) are on contrary aspect C = N.
Geometrical isomerism in N = N compounds.
Geometrical isomerism in cyclic compounds – e.g.- di-substituted cycloalkanes.
Optical isomerism
Plane polarized mild has vibrations simplest in a single aircraft. Optically lively compounds rotate aircraft polarized mildly. Angle of rotation (α) is the perspective via which aircraft polarized mild is circled while exceeded via the answer of optically lively substance. It is measured through a polarimeter. Specific rotation is the perspective of rotation produced through an answer of period 10 cm (or 1 dm) and having unit concentration (1 g/cm3) for a given wavelength (λ) of mild at given temperature (t). Particular rotation α wave period
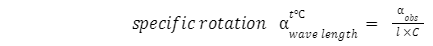
Isomers have equal bodily and chemical homes however have specific behavior toward aircraft polarized mild. Conditions for compound to reveal optical isomerism Compound ought to have as a minimum one uneven or chiral carbon atom. Compound ought to now no longer have aircraft of symmetry. Enantiomers are pairs of optical isomers which might be associated as non-excellent imposable photos of every different. They have equal homes however their behavior toward aircraft is mild. Diastereomers are pairs of optical isomers which can not be associated as non-excellent imposable photos of every different. They have specific bodily homes. Meso compounds do now no longer display optical hobby notwithstanding presence of chiral carbon atom because of presence of molecular symmetry. It is referred to as inner compensation. Substituted allenes (>C=C=C<) and substituted biphenyls (C6H5−C6H5) do now no longer have uneven carbon atom however they display optical isomerism because of chirality (dissymmetry) in molecule. Asymmetric synthesis is synthesis of optically lively compound from an optically inactive molecule. Walden inversion is conversion of d-shape of an optically lively compound into its l-shape or vice-versa. Resolution is separation of d and l bureaucracy from racemic aggregate. Racemisation is manner of formation of racemic aggregate through including 50% d & 50% l-shape of equal compound.
R and S configuration of optical isomers (advanced through Cahn, Ingold-Prelog)
Assign precedence to companies connected to chiral carbon atoms (as 1, 2, three, 4) according to series regulations. Arrange companies/atoms in one of these manner that institution having lowest precedence is directed far from us. If going from institution of maximum precedence to lowest precedence, eye actions in clockwise direction, it’s miles assigned configuration R(right) and if it actions in anti-clockwise direction, it’s miles assigned S (sinister or left).
Steric Hindrance
In natural compounds, numerous atoms or companies of atoms are organized in geometric style approximately every carbon atom. As lengthy as neighboring atoms or companies of atoms are at a distance more than the sum in their van der Waals radii, they do now no longer intervene with each other. However, while the space among neighboring atoms or companies of atoms is much less than the sum in their van der Waals’ radii, they repel every different because of spatial crowding. This pressure of repulsion because of proximity in area is referred to as steric dilemma (or steric pressure or van der Waals’ pressure). Molecules having steric pressure are much less solid than the molecules having no pressure. For instance, steric dilemma is gift within the cis isomer of however-2-ene however now no longer in Trans-isomer because of proximity of methyl companies
Conclusion
We recognize that an natural molecule is a complicated molecule that consists of numerous factors which might be bonded with carbon and carbon is an exceedingly flexible detail which could shape bonds with many factors, inclusive of hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen or it is able to additionally shape bonds with different carbon atom in order that it can shape massive carbon chains. And to emphasize the variety of bonds fashioned through the electrons in any molecule, the structural illustration is important.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






