The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, according to this theory. The elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers, so that elements with comparable properties are grouped together in the same column. Is arranged according to electron configuration.
The periodic table was used to forecast the chemical and physical properties of elements in the gaps on the table before all naturally occurring elements were known despite the fact that the table can no longer be used to predict attributes of yet-to-be-found elements, it can now be used to forecast attributes of elements that have yet to be discovered. All of these new elements are highly radioactive and break down into more familiar elements very rapidly. The table is currently useful to modern students and scientists since it helps determine the future. The types of chemical reactions in which a given element is likely to take part.
Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table, often known as the long version, is based on the modern periodic law. The table is a list of elements arranged in ascending order of their atomic numbers. The periodic table in its current form is known as the contemporary periodic table. It has 18 vertical columns and seven horizontal rows.
Modern periodic law
The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, according to the modern periodic law.
From left to right, scientists arranged elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers across each row. And it was discovered that elements with equal qualities repeated at regular intervals.
Modern Periodic Table Groups
- In the modern or long form of the periodic table, groups are the vertical columns.
- The periodic table is divided into 18 groups.
- These groupings are numbered one through eighteen.
- Each group is made up of components with the same electrical arrangement on the outer shell.
Periods in the Modern Periodic Table
- In the modern or long form of the periodic table, periods are the horizontal rows.
- The periodic table has seven periods.
- From top to bottom, they are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
- Only two elements make up the first period: hydrogen and helium.
- The second and third periods each have eight elements.
- The 6th period, on the other hand, has 32 elements.
- Four new elements have been added to the periodic table’s seventh period. 113-Nihonium, 115-Moscovium, 117-Tennessine, and 118-Oganesson are the elements. With 32 elements, this addition brings the 7th phase to a close.
- A separate panel at the bottom of the lengthy version of the periodic table. The lanthanides are a group of 14 elements that date back to the sixth period. The actinides are a group of 14 elements in the seventh period.
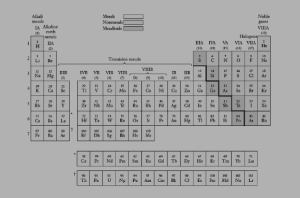
Figure: 1 Modern Periodic Table
Periodic Table of elements
The periodic table, commonly known as the periodic table of (chemical) elements, is a table that displays the chemical elements in a tabular format. It’s commonly used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and it’s considered a chemistry icon. It’s a visual description of the periodic law, which states that chemical elements’ properties are correlated with their atomic numbers in a predictable way.
Elements into groups
Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are the six noble gases that occur at the conclusion of the six completed periods and make up the periodic system’s Group 18 (zero) group. Horizontal series of components in the table are referred to as periods, and vertical series are referred to as groups. The atoms lithium and fluorine, as well as their equivalent elements sodium and chlorine, are divided into seven groups: 1 (Ia), 2 (IIa), 13 (IIIa), 14 (IVa), 15 (Va), 16 (VIa), and 17 (VIIa). The 17 elements of the fourth period, ranging from potassium to bromine, have distinct properties and are grouped together in the periodic system as Groups 1–17 (Ia–VIIa).
The alkali metals, the first group, thus comprises, in addition to lithium and sodium, the metals from potassium to francium down the table, but not the much less related metals of Group 11. (Ib; copper, etc.). Beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium are included in the second group, the alkaline-earth metals, but not the elements of Group 12. (IIb). The boron group includes elements from Group 13 of the periodic table (IIIa). The following are the other four groups: Carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium make up the carbon group 14 (IVa); nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and moscovium make up the nitrogen group 15 (Va); oxygen, sulphur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, and livermorium make up the oxygen group 16 (VIa);.
Importance of Periodic Table
- To summarise, the periodic table is significant because it is organised to provide, in a single, easy-to-understand reference, a wealth of information regarding elements and their relationships.
- The table can be used to make assumptions about the properties of elements that have yet to be found.
- Elements with comparable qualities are represented by columns (groups) and rows (periods).
- The table clearly shows and understands patterns in element attributes.
- The table contains crucial information for balancing chemical equations.
Conclusion
To summarise, the periodic table is significant because it is organised to provide, in a single, easy-to-understand reference, a wealth of information regarding elements and their relationships. The table can be used to make assumptions about the properties of elements that have yet to be found. The periodic table was used to forecast the chemical and physical properties of elements in the gaps on the table before all naturally occurring elements were known. Despite the fact that the table cannot be used to predict attributes of yet-to-be-found elements, it may now be used to anticipate attributes of elements that have yet to be discovered. All of these new elements are highly radioactive and break down into more familiar elements very rapidly. The table is currently useful to modern students and scientists since it helps predict the types of events that will occur of chemical reactions in which a given element is likely to take part.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






