Introduction
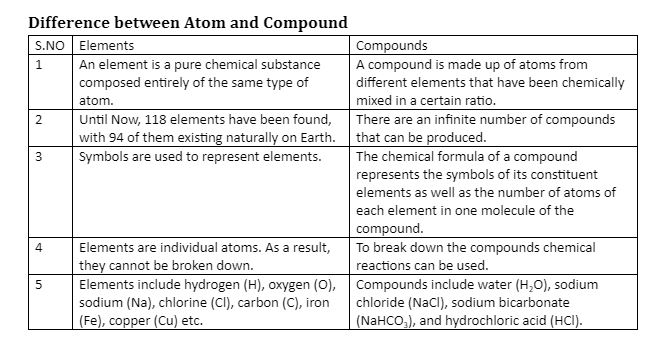
Elements and compounds are pure chemical substances that are found in our nature. The distinction between an element and a compound is that an element is a material composed of the same kind of atoms, but a compound is composed of various elements in certain proportions. Elements include iron, copper, hydrogen, and oxygen. Water (H2O) and salt (Sodium Chloride – NaCl) are two examples of compounds.
On the Periodic Table, elements are listed according to their atomic number. 94 of the 117 known elements, such as carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, exist naturally. 22 are artificial and have experienced radioactive alterations.
The reason for this is their instability, which causes radioactive decay over time, giving rise to new elements such as uranium, thorium, bismuth, and so on. Elements mix in set ratios to produce stable compounds thanks to chemical bonds that aid in compound formation.
What is Element?
Elements are defined as a set of atoms with an identical number of protons in their nuclei. These components are of a pure nature. A pure element has the same atomic number or a similar number of protons in its nucleus as another element. A total of 118 elements have been found so far, and they are organised in a periodic table based on their atomic numbers.
Classification
Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are the three primary categories of elements.
Metals: The greatest amount of elements in a periodic table is metal. Alkaline metals, transition metals, alkaline earth metals, and other metals are also included in this category. In periodic tables we can see Metals on the left side.
Nonmetals: Nonmetals are found on the right side of the periodic table and are extremely rare. Non-metals also include noble gases and halogens.
Metalloids: Metalloids are elements with characteristics that fall between nonmetals and metals. They are also known as semimetals. They are generally coloured as yellow on the periodic table and cover a staircase structure.
Example
Hydrogen, iron, aluminium, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, silicon, boron, sodium, and others.
Compound
A compound is a pure material made up of atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded to one another in a certain proportion.
As a result, it may be broken down into simpler components only by chemical processes. Compound qualities differ from the attributes of their separate constituents. The smallest unit of the compound is termed a molecule. In chemistry, the hydrogen element produces the most compounds.
Water, for example, is represented by the chemical formula H2O. It has a mass ratio of 2:16 or 1:8 of the elements hydrogen and oxygen.
Rain, rivers, the sea, wells, and lakes are some of the places where water can be acquired. The two elements are present in the same fixed ratio, i.e., 1:8 by mass, in pure water from any source. Salt, sugar, sand, carbon dioxide, washing soda, chalk, alcohol, and other substances are also compounds.
Classification of Compounds
Compounds are classified into two types based on their origin. These are organic and inorganic compounds, respectively.
- Inorganic compounds are those compounds that are obtained mainly from non-living sources such as rocks and minerals.
Examples: Common salt, stone, washing soda, baking soda, carbon dioxide, ammonia, sulphuric acid etc.
- The term organ refers to a variety of organs found in living creatures. As a result, organic compounds are those originating from living things like plants and animals. Carbon has been recognised as an essential constituent of all organic compounds. Organic substances are often known as carbon compounds.
Example: Methane, ethane, propane, alcohol, acetic acid, sugar, proteins, oils, and fats etc
Compounds are categorised into three groups based on their properties.
- Acid: Acids are sour chemical compounds that react with water to turn blue litmus paper red. Acids are sour chemical compounds that react with water to turn blue litmus paper red.
Example: hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, carbonic acid, lactic acid, and others.
- Bases: A base is a bitter chemical compound that, when mixed with water, turns red litmus paper blue.
Example: sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, and others.
- Salts: A salt is a compound formed by the interaction of an acid and a base.
Example: sodium chloride, calcium chloride, calcium nitrate, zinc sulphate, and others.
Conclusion
The distinction between an element and a compound is that an element is a material composed of the same kind of atoms, but a compound is composed of various elements in certain proportions. The distinction between an element and a compound is that an element is a material composed of the same kind of atoms, but a compound is composed of various elements in certain proportions. Water and salt are two examples of compounds. Elements are defined as a set of atoms with an identical number of protons in their nuclei. A total of 118 elements have been found so far, and they are organised in a periodic table based on their atomic numbers. A compound is a pure material made up of atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded to one another in a certain proportion.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




