The structure that results from examining the order and similarity of chemical components is known as a periodic system of chemical elements. A periodic table is a representation of the periodic system in another space, usually bi-dimensional. The observed oscillation of various chemical element properties as a function of the atomic number Z is referred to as periodic law.
For chemical elements, there is no single periodic system because they are dependent on the considered elements as well as the establishment of similarity and order. Similarly, the periodic law’s intended universality to all properties of chemical elements does not hold, because some qualities do not oscillate with Z.
Modern Periodic Table
Mendeleev’s periodic law and periodic table were used to create the contemporary periodic table. Mendeleev developed his periodic table in the late 18th century.
The modern periodic table, also known as the long version, is based on periodic law. The table is a list of elements arranged in ascending order of their atomic numbers. The periodic table in its current form is known as the modern periodic table. It has 18 vertical columns and seven horizontal rows. The chemical elements are ordered in order of increasing atomic number, or the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which corresponds to increasing atomic mass from left to right and top to bottom.
Modern periodic law
The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, according to the modern periodic law. Scientists arranged elements in ascending order of atomic number from left to right across each row. And it was discovered that elements with comparable qualities recur at regular intervals.
Structure of The modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table, often known as the long version, is based on the modern periodic law. The table is a list of elements arranged in ascending order of their atomic numbers. The current periodic table is referred to as the modern periodic table. It has 18 vertical columns and seven horizontal rows.
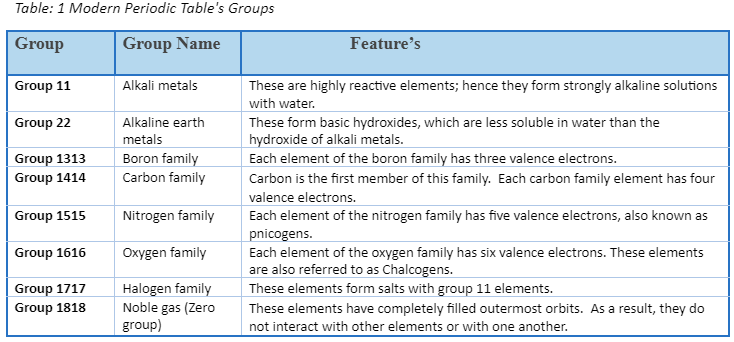
The Modern Periodic Table’s Groups
- In the modern or long form of the periodic table, groups are the vertical columns.
- The periodic table is divided into 18 groups.
- These groupings are numbered one through eighteen.
- Each group is made up of components on the outer shell that have the same electrical arrangement.
Modern Periodic Table Periods
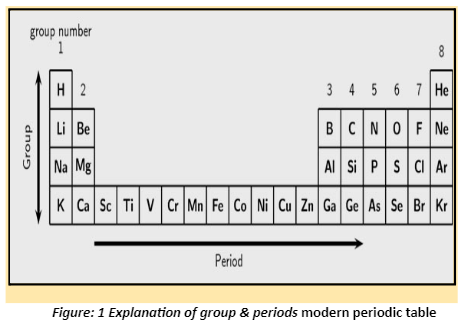
- In the modern or long form of the periodic table, periods are the horizontal rows.
- There are seven periods in the periodic table.
- From top to bottom, they are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
- Only two elements make up the first period: hydrogen and helium.
- The second and third periods each have eight elements.
- There are 18 elements in each of the 4th and 5th periods.
- The 6th period, on the other hand, has 32 elements.
- Four new elements have been added to the periodic table’s seventh period. 113-Nihonium, 115-Moscovium, 117-Tennessine, and 118-Oganesson are the elements. With 32 elements, this addition brings the 7th phase to a close.
- A separate panel at the bottom of the lengthy version of the periodic table. The lanthanoids are a group of 14 elements from the 6th era.
- The number of shells or energy levels in an atom of an element is represented by each period.
Types of elements in Modern Periodic Table
- Main group or representative elements: The elements found in groups 1 and 2 on the left side of the periodic table and groups 13 to 17 on the right side are referred to as main group or representative elements.
- Noble gases: These elements are found in Periodic Table Group 18 and have completely filled outermost shells, making them non-reactive.
- Transition elements: These elements are found in the middle block of the periodic table (Groups 3 to 12) and have two outermost shells that are incomplete; as a result, they change from most electropositive elements to most electronegative elements. As a result, they are referred to as transition elements.
- Inner transition elements: These are placed in two separate rows at the bottom of the periodic table to prevent the periodic table from expanding. There are two series, each with 14 elements. The first series, known as lanthanoids, contains elements 58 to 71. (Ce to Lu). The actinides are the second series of 14 rare-earth elements. It is made up of 90 to 103 elements (Th to Lr).
- Metals: Metals are located on the periodic table’s left side. Alkali metals are group one metals, and alkaline earth metals are group two metals.
- Non-metals: Non-metals are found on the periodic table’s right side.
- Metalloids: Metalloids are elements that exhibit both metal and nonmetal properties. They are found along the diagonal line beginning with group 13 (Boron) and ending with group 16. (Polonium).
Conclusion
Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, created the framework for the modern periodic table in 1869, leaving gaps for elements yet to be discovered. If, after arranging the elements according to their atomic weight, he discovered that they did not fit into the group, he would rearrange them.
The periodic table is significant because it is organised to provide a wealth of information about elements and their relationships to one another in a single, easy-to-access reference. The table can be used to predict the properties of elements.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






