Fundamental accounting assumptions are the basic assumptions that accountants use in their work. They are made up of three key concepts: Concern, Consistency, and accrual basis. The fundamental accounting assumptions are the most basic assumptions made by accountants during their work. In the past, accountants made assumptions based on their past experiences and judgement. These assumptions were then tested over time to see if they were valid. Today, these fundamental accounting assumptions align with what companies want to achieve with their accounting practices.
Defining Accounting Assumptions?
Accounting assumptions are the guidelines that accountants use when they prepare financial statements. They are used to ensure that the statements are in line with the law and other regulations.
An accounting assumption is a belief or opinion of an accountant, and it is not necessarily true. For example, an accountant may believe that a company’s assets will always be worth more than what they cost because of depreciation costs. This is an accounting assumption because it is not necessarily true for all companies.
Fundamental accounting principles are the underlying assumptions used to calculate financial statements. These fundamentals are not subject to change, so they serve as a stable reference point for all future transactions.
What are the Main Types of Accounting Assumptions?
Fundamental accounting assumptions are of different types, which are mentioned below. The entity’s reporting period is a calendar year. The entity has at least one business segment, and there is no significant difference between assets and liabilities.
A company has all its assets at the beginning of its reporting period. It does not have any liabilities or contingent liabilities that may arise during its reporting period. Furthermore, it does not have any long-term investments or other assets that are not available for use during its reporting period.
- Going Concern
Going concern is a fundamental accounting assumption made when a company’s financial statements are prepared. It reflects the company’s ability to continue operating in the future.
The most common form of going concern assumption is that the company will continue to generate sufficient cash flows from its ongoing operations to meet its obligations and provide for its future needs.
- Consistency
Consistency is the cornerstone of accounting. It is a concept that can be defined as the degree to which one set of accounts or financial statements is identical.
The fundamental accounting assumptions are the assumptions made to generate financial statements according to generally accepted accounting principles.
This assumption states that procedures followed in accounting remain the same until they are in contradiction to any specified accounting rules, methods, standards, etc.
- Accrual
Accrual is a fundamental accounting assumption that the amount of revenue or expense recognized in a period should equal the amount of revenue or cost incurred during that period.
The accrual principle is an essential accounting assumption because it recognises all revenues and expenses over time.
According to this assumption, accounting transactions are recorded in the books of accounts when they occur. In contrast to the cash system, revenue and expenditure are recognized in the year they are realised in the accrual approach.
Difference between a Basic & Comprehensive Statement of Financial Position?
A basic statement of financial position is a snapshot of the company’s financial situation at a point in time. This includes its assets, liabilities, and net worth. A comprehensive statement of financial position is a report that provides a more detailed assessment of what the company is doing.
The difference between these two statements is that the comprehensive statement provides information on how much cash reserves are available to cover future obligations and other commitments. It also includes information on its ability to raise funds through debt or equity markets and other sources.
Parameters of Accurate Assumptions
Assumptions are used to simplify complex processes. However, they can become a liability if they are not accurate. There are certain vital questions that you should ask when analysing financial statements to ensure that your assumptions are correct.
- What is the company’s focus?
- What is the company’s target market?
- What is the company’s current business strategy?
- How does the company plan on reaching its target market?
Conclusion
An accounting assumption is a notion or opinion held by an accountant that isn’t always correct. Because of depreciation charges, an accountant may feel that a company’s assets will always be worth more than what they cost. This is an accounting assumption because it does not apply to all businesses. Fundamental accounting assumptions or concepts are the set of assumptions that are made when preparing financial statements. This includes the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. The role of fundamental accounting assumptions is to provide a framework for understanding financial statements.
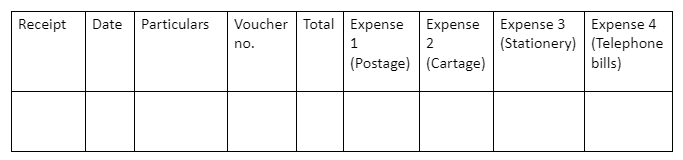
Types of Petty cash book
There are two types of petty cash books. These are
- Simple petty cash book
- Analytical petty cash book
Simple petty cash book
It is similar to that of the original petty cash book. The cash that is received is written under the debit section of the cash book. Payments made by the petty cashier are recorded on the credit side of the book.
Analytical petty cash book
A separate column is given to each petty expense on the credit side in an analytical petty cash book. Whenever a petty expense is recorded in the total payment column, the same amount is recorded in the specific petty expense column.
An analytical petty cash book is the most reliable and effective recording of petty expenses.
Conclusion
A petty cash book is a record of minor cash expenditures, that are sorted by month and date. It is a type of ledger book, in most cases. The Imprest system of petty cash books is regarded as one of the most used systems for maintaining a cash book. There are two types of petty cash books. One of these two is called the simple petty cash book, and the other is the analytical petty cash book. The petty cash book format is very important to keep in mind while preparing one, as it ensures the accuracy and reliability of transactions so recorded. The petty cash book format is very important to consider while preparing a petty cash book.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






