A data structure is a type of data storage, organisation, and processing format. There are numerous basic and complex data structures available, all of which are designed to organise data for a specific purpose.
People can easily find and use the information they need thanks to data structures. Data structures, above all, describe how information is organised so that machines and humans can better interpret it.
What is data structure ?
A data structure is a type of data storage, organisation, and processing format. There are numerous basic and complex data structures available, all of which are designed to organise data for a specific purpose. People can easily find and use the information they need thanks to data structures.
Types of Data Structure:
Data structures are divided into two categories:
Linear data structure: A linear data structure is one in which the data structure’s elements produce a sequence or a linear list. Arrays, Linked Lists, Stacks, Queues, and other types of data structures are examples.
Non-linear data structure: A non-linear data structure is one in which the elements of the data structure result in nodes not being traversed in a sequential manner. Trees, graphs, and other examples
Notes on Data Structures for GATE:
In the field of computer programming, data structure is a large subject. This is an extremely broad issue that is also really significant. Students who plan to take the GATE examination in this topic should study data structures in depth.
In computer science, the topic Data structures is divided into multiple subtopics, or we can say that there are various types of data structures.
Problem-Solving Procedures in Data Structures and Algorithm
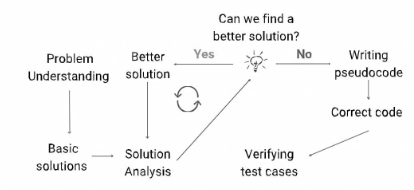
Developing a strategy for comprehending the issue:
1.Consider a proper basic solution.
2.Designing step-by-step pseudocode solution.
3.Analyzing the efficiency of a solution.
4.Optimizing the solution further.
5.Transforming pseudocode into a correct code.
Questions & Answers on Data Structure
1.The “Sum of n Natural Numbers using Recursion” is the topic of this set of Data Structure Questions and Answers for Aptitude Test.
- Which of the following statements about natural numbers is incorrect?
- a) The Iteration method can be used to find the sum of the first n natural numbers.
- b) The recursion method can be used to determine the sum of the first n natural integers.
- c) The Binomial coefficient approach can be used to get the sum of the first n natural integers.
- d) There is no formula for calculating the sum of the first n natural numbers.
Answer: d
Explanation: To find the sum of the first n natural numbers, apply any of the methods listed above.
- Which of the following produces the first n natural numbers’ sum?
- a) nC2
- b) (n-1)C2
- c) (n+1)C2
- d) (n+2)C2
Answer: c
Explanation: n*(n+1)/2 equals (n+1)C2, which is the sum of the first n natural integers.
Data structures and algorithms coding questions and answers
- Could you describe the distinction between file and storage structure?
A file structure representation is the representation of data into secondary or auxiliary memory, such as a hard disc or a pen drive, that saves data that remains intact unless deliberately erased.
Data is kept in the main memory, i.e. RAM, and is then destroyed once the function that uses it has completed.
The distinction is that data in a storage structure is saved in the computer system’s memory, but data in a file structure is stored in the auxiliary memory.
- How are linked lists more efficient than arrays?
Deletion and insertion
In an array, the insertion and deletion processes are costly since space must be made for new elements and current elements must be relocated.
In a linked list, however, the identical procedure is simplified because we merely update the address in the node’s next pointer.
Data Structure that Changes:
Because a linked list is a dynamic data structure, it does not require an initial size because it can grow and shrink at runtime by allocating and deallocating memory.
The size of an array is limited because the number of items is stored statically in main memory.
There will be no memory waste.
Because a linked list’s size can increase or decrease depending on the program’s demands, no memory is wasted because it is allocated at runtime.
When declaring an array of size 10 and only storing three elements in it, the space for three elements is wasted. As a result, arrays have a higher risk of memory waste.
Conclusion
Most computer programming languages’ standard base data types, such as integers or floating-point values, are insufficient to convey the logical intent for data processing and application. In order to facilitate processing, programmes that ingest, manipulate, and output data must understand how data should be arranged.
Data structures connect data pieces in a logical way, allowing for more efficient data use, persistence, and sharing. They give a formal model that explains the organisation of data items.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






